Understanding Commodity Prices
Understanding Commodity Prices: How Commodity Prices Affect The Economy
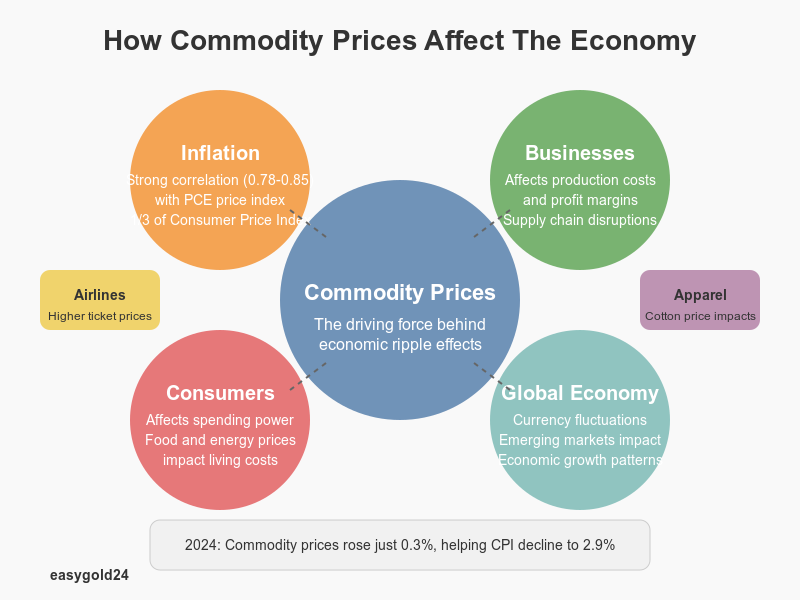
Commodity prices ripple through the global economy, shaping everything from consumer costs to business operations. Their influence extends far beyond trading floors, creating a complex web of economic relationships that affect our daily lives.
Link to inflation
The relationship between commodity prices and inflation runs deep, with commodities comprising more than one-third of the Consumer Price Index. Data shows a strong positive correlation between commodity prices and the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index. When commodity price data is lagged by three to five months, the correlation increases to 0.78 with the PCE index and 0.85 with the PCE nondurable sector.
Agricultural, food, and energy commodities have a particularly substantial effect on inflation compared to other commodities. The pass-through of commodity prices to inflation varies notably across different economic environments. During periods of high inflation, commodity prices play a more substantial role in driving the inflation process.
Recent trends illustrate this connection clearly. After reaching a peak of 9.1% in June 2022, the Consumer Price Index declined significantly, standing at 2.9% by the end of 2024. Throughout 2024, commodity prices as a whole rose just 0.3%, contributing to this moderation in inflation.

Impact on businesses
Businesses face multiple challenges when dealing with fluctuating commodity prices. For manufacturers and retailers, these price changes directly affect production costs and profit margins. When oil prices increase, companies must either absorb the rising fuel costs or attempt to pass them along to consumers, potentially affecting their bottom line.
The effects cascade through various industries:
- Airlines typically transfer part of increased fuel costs to consumers through higher ticket prices.
- Apparel retailers’ costs fluctuate with cotton price changes.
- Food manufacturers face varying input costs based on agricultural commodity prices.
- Jewelry retailers’ profitability links closely to precious metal prices.
Supply chain disruptions compound these challenges. In 2021, sea freight costs reached their highest levels since the 2008 financial crisis, while container rates surged due to global demand recovery and port congestion. Weather-related events further complicated matters, affecting markets for many raw materials and raising prices across commodities of all types.
Effect on consumers
Commodity price fluctuations significantly affect consumer spending and living costs. When food prices rise, the effects ripple through the entire supply chain. For example, higher wheat prices increase livestock feed costs, subsequently raising meat prices for grocery stores and consumers.
The impact on food security presents a particularly pressing concern. The World Food Program estimates that 345 million people in almost 80 countries will face acute food insecurity this year—more than double the number in 2020. This situation stems in part from recent price surges, with world food commodity prices rising nearly 40% in the two years before Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Energy prices particularly affect consumer budgets through multiple channels:
- Direct costs for heating and transportation
- Indirect effects on manufactured goods prices
- Impact on food production through fertilizer costs
Recent data indicates that commodity markets remain heterogeneous in their effects on different economies. Policy frameworks increasingly enable countercyclical macroeconomic responses, becoming more common and beneficial in managing these impacts. Additionally, the relationship between economic growth and commodity demand varies significantly across countries, depending on their stage of economic development.
Currency fluctuations can intensify the impact of commodity prices, particularly in emerging markets and developing economies. These nations often face heightened vulnerability to commodity price volatility, especially those heavily dependent on primary commodity exports.
Understanding Price Trends in 2025
The global commodity landscape in 2025 presents a complex picture, marked by shifting market dynamics and price fluctuations in various sectors. Investors and analysts closely monitor these movements, and several key trends emerge that shape the current market conditions.
Current market conditions
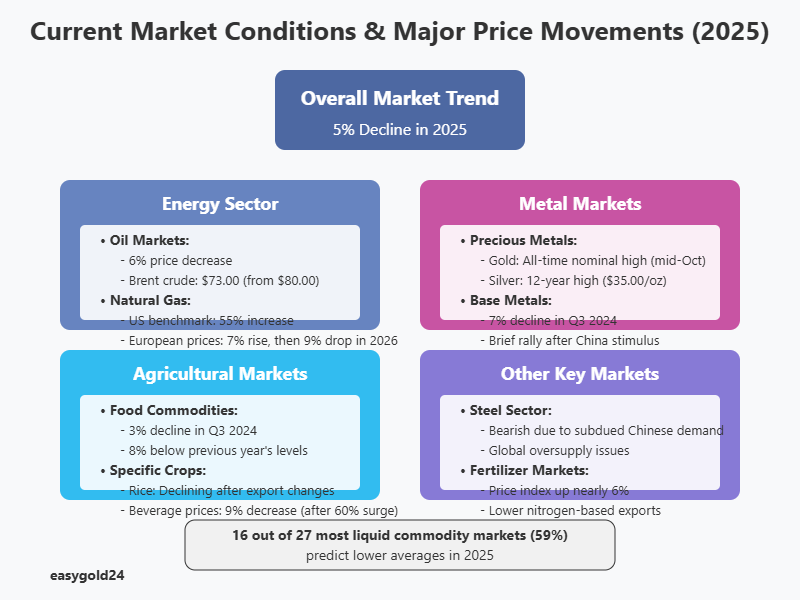
Commodity markets show a broad decline, with prices predicted to fall by 5% in 2025. This downward trend stems from multiple factors, including moderate economic growth in major economies and evolving supply-demand dynamics.
The energy sector exhibits notable changes, as the price index predicts a 6% decrease in 2025. Oil markets remain in considerable surplus, with Brent crude prices averaging USD 73.00 per barrel, down from USD 80.00 in 2024. Global oil consumption shows modest growth, increasing by approximately 0.9 million barrels per day.
Natural gas markets demonstrate interesting regional variations. The U.S. benchmark predicts a substantial 55% increase in 2025, driven by strengthening global LNG demand. European gas prices project a 7% rise before declining by 9% in 2026.

Metal prices reveal a nuanced outlook. After experiencing a 7% decline in the third quarter of 2024, prices briefly rallied following China’s late-September stimulus measures. Base metal prices, primarily aluminum and copper, remain sensitive to shifts in global industrial activity.
Agricultural markets present a mixed scenario. Food commodity prices declined by 3% in the third quarter of 2024, positioning them 8% below their previous year’s levels. Record-high production of maize, rice, soybeans, and wheat in the 2023-24 season contributes to this trend.
Major price movements
Several commodities demonstrate significant price shifts throughout 2025:
Gold markets have achieved remarkable milestones, reaching an all-time nominal high in mid-October. This surge reflects:
- Heightened geopolitical tensions
- Sustained central bank purchases
- Predicted shifts toward easing U.S. monetary policy
The steel sector faces bearish conditions due to:
- Subdued demand in China’s steel-intensive property sector
- Oversupply in global markets
- Cheap exports flooding neighboring emerging market economies
Agricultural commodities display distinct patterns:
- Rice prices show a declining trend following the easing of Indian export restrictions
- Maize and wheat prices indicate potential increases from current levels, albeit remaining below 2021-2023 benchmarks
- Beverage prices project a 9% decrease after experiencing a 60% surge in 2024
The crude oil market demonstrates heightened volatility. Brent prices averaged USD 75.00 per barrel during September-October, marking the lowest levels since June 2023. This volatility stems from shifting geopolitical risk assessments, signs of subdued economic growth in China, and ample supply conditions.
Looking at broader market indicators, 16 out of 27 of the most liquid and valuable commodity markets (59%) predict lower averages in 2025. The Aggregate Commodity Price Index projects a 1% decline, following a 2% year-on-year growth in 2024.
Natural gas markets present regional divergences. U.S. prices remain stable amid robust domestic production, but LNG prices increased by 8%. European benchmarks surged by 15% in the third quarter of 2024, driven by intensified competition for LNG imports.
Precious metals maintain their strong performance. Silver reached a 12-year high of almost USD 35.00 per ounce. This trend receives support from continued central bank buying (primarily led by China), investors seeking safe-haven assets, and heightened geopolitical risks.
The fertilizer sector shows notable movement, with the price index rising nearly 6% because of lower-than-expected nitrogen-based exports. This increase potentially affects agricultural production costs and, subsequently, food commodity prices moving forward.
Future Outlook for Commodity Prices
As global markets evolve, commodity prices in 2025 and beyond paint a complex picture of supply, demand, and emerging challenges. The interplay between various economic forces shapes a dynamic landscape that requires careful analysis and strategic planning.
Expected trends
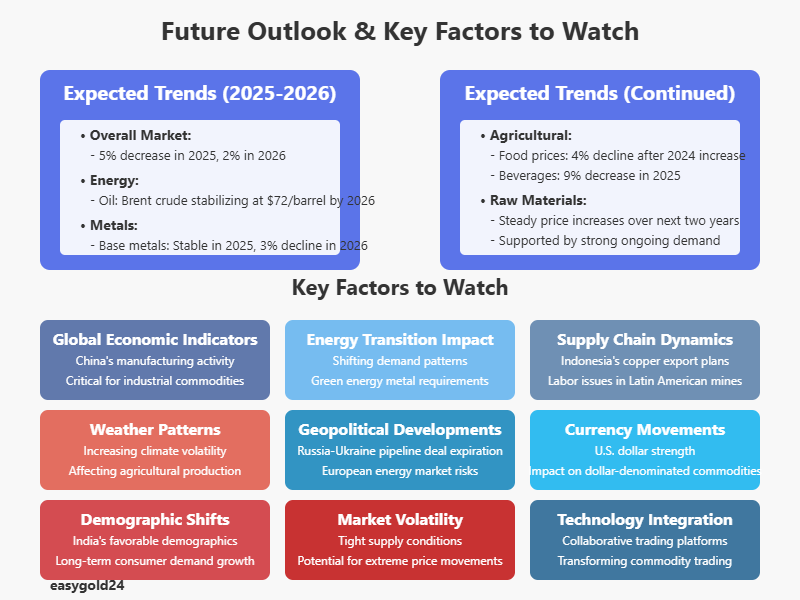
The commodity market predicts broad-based price declines, with projections indicating a 5% decrease in 2025, followed by an additional 2% reduction in 2026. This trend reflects several underlying shifts across different commodity sectors.
In the energy sector, prices show distinct patterns:
- Oil markets maintain considerable surplus, with Brent crude prices expected to stabilize at USD 72.00 per barrel by 2026
- Natural gas prices exhibit regional variations, as U.S. standards predict a 55% surge in 2025
- European gas markets expect a 7% increase in 2025, although prices may decline by 9% in 2026
Agricultural commodities showcase evolving dynamics throughout 2025. Food prices predict a 4% decline after a slight increase in 2024. This adjustment stems from improved supply conditions across major crop categories. Beverage prices, although currently elevated, project a 9% decrease next year.
Raw materials present a contrasting outlook, as prices steadily climb over the next two years, supported by strong demand. Market participants must prepare for divergent trends across different commodity categories.
Metal markets reveal interesting developments. Base metal prices indicate stability in 2025, although a 3% decline looms in 2026. This trajectory reflects moderate industrial activity growth in major economies, specifically China. Iron and steel prices remain stable, yet nickel and copper predict faster price increases.
Key factors to watch
Several critical elements warrant close attention as they shape commodity markets moving forward:
Global Economic Indicators
The pace of global economic growth emerges as a fundamental driver. Industrial commodity prices remain particularly sensitive to China’s economic performance. Manufacturing activity indicators, such as China’s official PMI rising above 50 points in October 2024, signal potential demand shifts.
Energy Transition Impact
The move toward low-carbon technologies creates profound changes in commodity demand patterns. This transition affects both traditional energy commodities and metals essential for renewable technologies. Copper and nickel markets specifically benefit from predicted interest rate cuts and investments in green energy.

Supply Chain Dynamics
Indonesia’s plans regarding copper exports, potential labor unrest in Latin American mines, and possible copper smelter closures in China present significant supply risks. These factors could tighten global supply chains throughout 2025.
Weather Patterns
Climate volatility increasingly influences commodity markets. Since 2019, weather volatility has shown a marked upturn, causing agricultural commodities to experience substantial production and price fluctuations. This trend predicts intensification over the next decade.
Geopolitical Developments
Political tensions remain a substantial near-term risk affecting multiple commodities. The expiration of the Russia-Ukraine pipeline deal in early 2025 heightens supply risks, particularly in European energy markets.
Currency Movements
The U.S. dollar’s strength continues to affect commodity prices. A weaker dollar typically inflates U.S. dollar-denominated commodities relative to foreign prices, boosting export competitiveness.
Demographic Shifts
Population dynamics, particularly in emerging markets, shape long-term demand trends. India’s favorable demographics suggest potential consumer demand growth in upcoming decades.
Market Volatility
Ongoing tightness in major commodity supplies indicates potential future shocks could trigger extreme price volatility. This situation requires enhanced risk management strategies across trading desks.
Policy Developments
Government interventions through strategic collaborations become increasingly significant. Commodity traders now work more closely with governments to ensure energy supply security and support new green value chains.
Investment Patterns
With substantial cash reserves available, senior executives face significant decisions regarding investment allocation. Strategic asset positions across legacy and emerging value chains demand careful consideration.
Technology Integration
The commodity trading sector undergoes technological transformation. Collaborative, tech-enabled trading platforms emerge as priority areas for development.
Navigating Commodity Markets in 2025
Commodity markets in 2025 are shaped by a range of factors, presenting both challenges and opportunities for investors. Price fluctuations across various sectors reflect global economic trends, including moderate growth and shifting supply-demand dynamics. In particular, precious metals like gold continue to exhibit strong performance, offering potential stability amid broader market changes.
The interconnectedness of commodities with inflation, business operations, and consumer prices emphasizes their crucial role in the global economy. As we move forward, understanding market influences such as geopolitical developments, climate change, energy transitions, and technological progress will be vital for navigating these markets effectively.

For those looking to invest in commodity markets, a flexible and informed approach is key. Understanding the intricate relationships between economic forces and maintaining a disciplined strategy will help investors capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks in this dynamic environment.
As Hartmann & Benz advances with its public listing on the OTCQB market, investors now have the opportunity to engage with our shares. Alongside this, we have launched the EasyGold security token, enabling investors to hold gold in a simplified and cost-effective manner. With continued growth and an eye on future opportunities, it’s an exciting time to stay informed and explore new avenues for investment.
