Portfolio Diversification
Mastering Portfolio Diversification: Build a Stable and Profitable Investment Strategy
Aggressive portfolio diversification strategies have demonstrated impressive returns—up to 136% in their best 12-month period. However, the same strategies also carry significant risks, as evidenced by a 61% loss during their worst periods. Achieving the right balance is essential for protecting your investments.
Research shows that a portfolio consisting of 25 to 30 stocks is the most effective way to reduce risk while ensuring strong returns. By diversifying across asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, you create a buffer against market volatility. The key is to include assets that move independently of each other, helping to stabilize your portfolio even in turbulent times.
Diversification helps manage risk while positioning your investments for long-term success. Whether you’re just starting or looking to refine your strategy, understanding how to spread risk effectively is the first step toward building a robust portfolio that works for you.
What is Portfolio Diversification
Portfolio diversification is a risk management strategy that involves mixing different investments in your portfolio. Instead of concentrating all your investments in one place, you spread your money across different assets and investment vehicles.
Simple concept explained
Think of portfolio diversification as distributing your investments across multiple baskets. Research shows that a well-structured portfolio of 25 to 30 stocks provides the most cost-effective way to reduce risk. This strategy combines different types of assets that respond uniquely to market conditions.
Diversification works by combining investments that react differently to market forces. Your overall portfolio performance remains balanced because some investments might increase in value when others decline. This approach reduces unsystematic risk, allowing positive returns from some investments to offset negative performance from others.

Why investors need diversification
Portfolio diversification does more than maximize returns. The strategy primarily focuses on managing and reducing portfolio risk. Here are the main benefits:
1. Risk Mitigation: By spreading investments across asset classes, industries, and maturities, your portfolio becomes more resilient against market shocks.
2. Enhanced Long-term Returns: Diversified portfolios typically outperform concentrated investments over time because they carry less risk.
3. Portfolio Stability: Your investments remain more stable during market swings, helping protect your capital, which becomes increasingly important as you approach retirement.
Nevertheless, diversification comes with trade-offs. While the strategy protects you from losses, it also limits potential gains in the short term. Additionally, managing multiple holdings requires more time and might lead to higher transaction costs.
Research shows diversification works best when securities in your portfolio have low correlation—meaning they react differently to market forces. This characteristic helps your portfolio remain stable even when certain market segments face turbulence.
A properly diversified portfolio captures market returns across asset classes while maintaining controlled risk exposure. Although diversification cannot eliminate all investment risk, it significantly reduces specific asset risks while potentially improving risk-adjusted returns.
Understanding Investment Risk Types
Your investment success largely depends on how well you understand and manage different portfolio risks. Let’s examine the main risk categories that shape investment decisions.
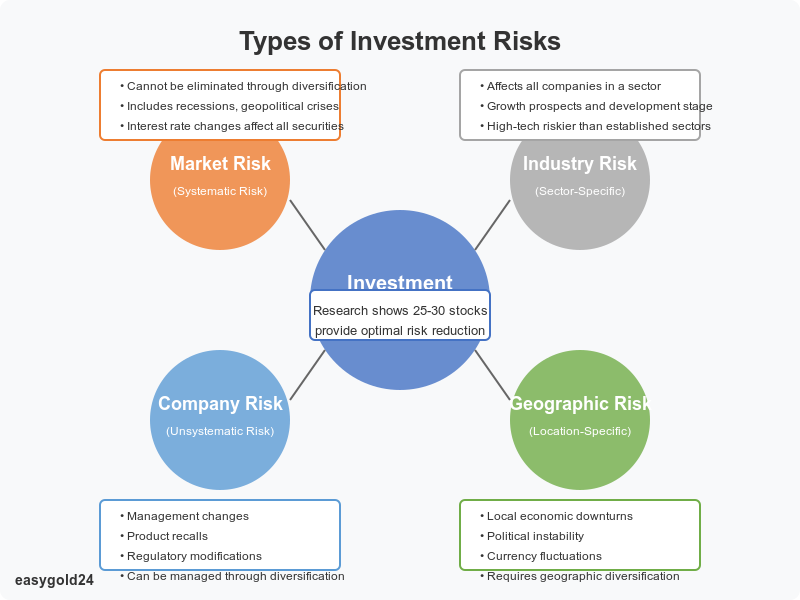
Market risk
Market risk, also known as systematic risk, affects all investments in financial markets and cannot be eliminated through diversification. Economic events such as recessions, geopolitical crises, or interest rate changes create this risk. The 2008 financial crisis illustrated how market risk caused widespread losses across almost all asset types.
Interest rates play a vital role in assessing market risk. Fixed-income securities typically lose value when interest rates rise. Securities with longer maturities experience larger price swings because each rate change substantially affects their present value.
Company risk
Individual businesses face company-specific risk, also called unsystematic risk. Several factors contribute to this risk:
- Management changes
- Product recalls
- Regulatory modifications affecting sales
- New market competitors
Unlike market risk, a well-diversified portfolio can effectively manage company risk. Public company executives often face higher company risk because their investment portfolios are heavily concentrated in their employer’s stock.
Industry risk
Specific sector factors create industry risk that affects all companies within that sector. Mature industries usually carry lower risk than emerging ones. A comprehensive assessment of industry risk examines:
- Growth prospects and development stage
- Sensitivity to macroeconomic changes
- Supplier and customer bargaining power
- Competitive environment
- Product substitution possibilities
Industry risk ratings range from very low to very high based on factors such as cyclicality and competitive dynamics. High-tech manufacturing typically carries higher industry risk than established sectors like textiles.
Geographic risk
Smart investors use geographic diversification as a vital strategy to manage location-specific risks. Spreading investments across regions and countries helps protect against:
- Local economic downturns
- Political instability
- Currency fluctuations
- Regional market challenges
Your portfolio becomes more stable when you invest in multiple geographic regions. During a U.S. and European recession, allocating some investments to faster-growing emerging economies might provide balance.
Geographic diversification requires careful risk assessment. Emerging markets offer higher growth potential but come with greater political risk and currency volatility. Exchange rates fluctuate constantly and can significantly impact your investment returns.
Core Asset Classes for Diversification
Your investment portfolio works best with three basic asset classes that balance risk and potential returns. A good understanding of these core elements helps build a strong investment strategy.
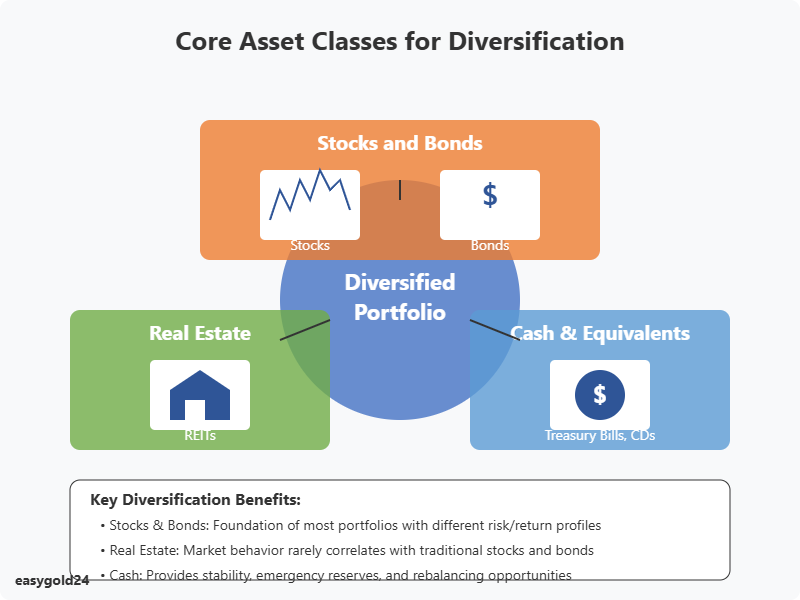
Stocks and bonds
Most investment portfolios are built on a mix of stocks and bonds. Stocks provide the best potential returns among major asset categories. Bonds are fixed-income securities that generate steady income with lower risks. Currently, bonds have a lower correlation with U.S. stocks than most other major asset classes.
Historically, stock and bond prices moved in opposite directions, which naturally protected portfolios. The correlation between these assets increased to approximately 0.6 during 2022-2023, up from a long-term average near zero. Despite this change, bonds still add stability to portfolios.

Real estate investments
Real estate is an excellent way to diversify because its market behavior rarely correlates with traditional stock and bond markets. Research shows that broad real estate exposure helps reduce portfolio volatility, allowing investors to achieve similar returns with less risk.
Here are the key benefits of real estate investments:
- Risk-adjusted returns improve with geographic spread across regions
- U.S. real estate equity and credit showed the highest absolute returns in the last decade
- Assets from Asia and Europe boosted risk-adjusted returns
The real estate market currently presents unique opportunities. Many equity owners need to sell assets, making high-quality properties in strong sectors available at attractive prices.
Cash and equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents help stabilize portfolios in several important ways:
- They serve as reserves to rebalance portfolios during market downturns
- They function as emergency funds for unexpected expenses
- They allow you to access capital quickly without selling other assets
Popular cash equivalents include:
- Money market funds
- Certificates of deposit (CDs)
- Treasury bills
- U.S. savings bonds
These instruments trade some yield for safety and liquidity. CDs usually offer higher interest rates than regular savings accounts, particularly with longer terms. Treasury bills, backed by the U.S. government, are highly liquid with minimal risk.
Inflation poses a significant risk to cash positions. The U.S. Dollar lost half its value between 1990 and 2018. Your cash allocation should be balanced against other more volatile assets in your diversified portfolio.
Assets with different performance patterns work together to enhance diversification benefits. This strategy often outperforms relying on just one asset class. By carefully selecting these core asset classes, your portfolio becomes more resilient to market swings while maintaining growth potential.
Building Your First Diversified Portfolio
Creating your first diversified portfolio represents a significant step toward financial stability. Consider these fundamental steps of successful portfolio diversification before beginning your investment journey.
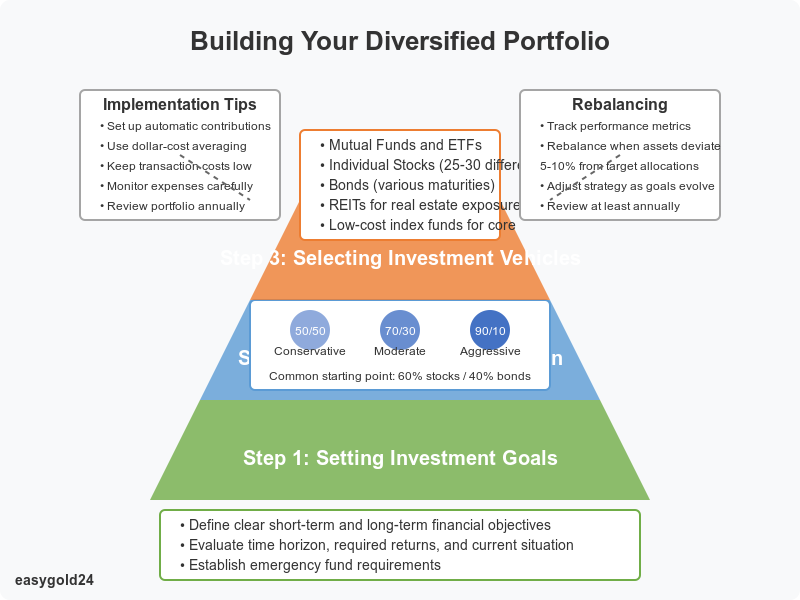
Setting investment goals
First, define clear financial objectives. Short-term goals might include buying a house within three years, while long-term goals typically focus on retirement planning. Your investment choices and risk tolerance directly stem from these goals.
The key factors you need to evaluate include:
- Time horizon for each investment goal
- Required returns to meet objectives
- Current financial situation
- Emergency fund requirements
Choosing asset allocation
Asset allocation serves as the foundation of portfolio diversification. Most investors begin with a 60% allocation to stocks and 40% to bonds. Your specific allocation depends on:
- Risk tolerance level
- Investment timeline
- Income requirements
- Market conditions
A 90% stocks and 10% bonds split works well for aggressive growth. Moderate investors usually choose 70% stocks and 30% bonds, while conservative portfolios maintain a 50-50 balance between stocks and bonds.
Selecting investment vehicles
After determining your asset allocation, select the right investment vehicles. Research shows that 25-30 different stocks provide the most affordable risk reduction. Consider these proven options:
- Mutual Funds and ETFs: These provide instant diversification across multiple securities
- Individual Stocks: Select companies from different sectors
- Bonds: Include different maturities and credit qualities
- Real Estate: REITs offer property exposure without direct ownership
Making your first investments
Implement your strategy by following these practical steps:
- Set up automatic investment contributions. Dollar-cost averaging reduces timing risk when you invest fixed amounts regularly.
- Maintain good investment documentation. Track performance metrics and perform annual rebalancing when asset classes deviate more than 5-10% from target allocations.
- Apply these proven practices:
- Use broad-market index funds for core positions
- Add sector-specific investments gradually
- Keep transaction costs low
- Monitor investment expenses carefully
Diversification requires ongoing attention. Review your portfolio at least annually to ensure it aligns with your financial goals. A well-diversified portfolio positions you for long-term success in all market conditions through careful selection and regular monitoring.
Common Diversification Mistakes
Even experienced investors make mistakes when balancing their investment portfolios. Understanding common diversification mistakes helps protect your investments from unnecessary risks and poor returns.
Over-diversification problems
Research shows that a well-balanced portfolio with approximately 20 unrelated stocks works best to diversify away market risk. Yet many investors fall into excessive diversification, which financial experts call “diworsification.”
Here are the biggest problems with over-diversification:
- Diluted Returns: When investments are spread too thin, the impact of high-performing assets on your overall portfolio diminishes. Too many investments mean that strong gains from individual holdings barely affect your bottom line.
- Management Complexity: A portfolio with numerous holdings increases your investment costs through additional transaction fees. Tracking performance and conducting proper research becomes increasingly difficult with numerous positions.
- Overlapping Investments: Investors often create redundancy by putting money in multiple funds that target similar markets or sectors. This approach increases costs without providing true diversification benefits.
Financial advisors sometimes contribute to over-diversification through:
- Spreading investments across multiple auto-diversification products
- Creating unnecessary portfolio turnover to generate commissions
- Using complex multi-manager investment products
Under-diversification risks
Insufficient diversification exposes your portfolio to unnecessary risk. Wharton finance professor Jeffrey Jaffe believes under-diversification remains one of the most significant threats to investment success.
These factors lead to under-diversification:
- Home Bias: Portfolios often concentrate in familiar assets or domestic markets. This habit creates geographic concentration risk and may limit returns while making you vulnerable to local market downturns.
- Company-Specific Risk: Employees often invest too heavily in their employer’s stock through company purchase programs. Examples like Enron and Lehman Brothers demonstrate how dangerous this approach can be.
- Correlation Oversight: Some investors confuse variety with diversification. Owning multiple assets that move in tandem during market changes defeats the purpose of diversification. For example, holding several precious metals may appear diverse but offers little protection since these assets often move together.
These proven strategies help avoid such pitfalls:
- Regular Portfolio Review: Check your investments frequently to maintain target allocation levels
- Correlation Analysis: Understand how different assets in your portfolio interact
- Professional Guidance: Consult multiple professionals before making significant portfolio changes
Proper diversification requires balance between too many and too few holdings. Studies show that excessive diversification leads to below-average risk-adjusted returns, while too few positions make you vulnerable to company-specific risks.
Portfolio Diversification: A Strategy for Long-Term Success
Building a resilient portfolio requires more than simply selecting a variety of assets. True diversification means thoughtfully allocating your investments across different asset classes—stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash equivalents—ensuring a balance that can withstand market volatility.
A well-diversified portfolio is essential for managing risk while positioning your investments for steady growth. Rather than focusing on perfect diversification, the key is to align your investments with your goals and risk tolerance. Regular portfolio reviews and adjustments will help you maintain the right balance as your financial situation evolves.
To maximize your portfolio’s potential, avoid over-diversifying, which could dilute returns, or over-concentrating in familiar assets that may expose you to unnecessary risk. A well-structured mix of diverse investments creates a solid foundation for long-term wealth growth.
As you refine your diversification strategy, remember that adaptability is crucial. Adjust your portfolio regularly, keeping an eye on market shifts, so your investments remain aligned with your objectives.
At Hartmann & Benz (EasyGold), we understand the importance of creating a diversified investment portfolio. With our upcoming listing on the OTCQB, we are offering new opportunities for investors to participate in the growth of the gold market through innovative solutions like the EasyGold security token. This token allows you to invest in gold without the complexities of physical storage while benefiting from the potential of a growing global market.
Explore how EasyGold can enhance your portfolio and provide a stable foundation for future growth.
