Geopolitics And Commodity Markets
The Hidden Connection: How Geopolitics Impacts Commodity Markets in 2025
Geopolitics plays a crucial role in shaping commodity markets, a fact clearly demonstrated when Russia invaded Ukraine in February 2022. The immediate spike in Brent oil prices by nearly 30% over just two weeks highlighted the vulnerability of markets to global political events.
While many analysts assume that political tensions automatically drive prices up, the reality is more nuanced. Data shows that, on average, global political shocks result in a 1.2% drop in oil prices after three months. However, when tensions stem from major oil-producing regions, prices tend to rise by 0.8% to 1.5% in the short term.
In 2025, commodity markets face new challenges, influenced by ongoing political events. From energy to precious metals and agricultural products, supply chain disruptions and price volatility will continue to affect markets worldwide. Understanding how these geopolitical events shape market trends is essential for developing strategies that can mitigate risk and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Stay informed, adapt to the evolving market landscape, and make decisions that align with the shifting geopolitical environment.
Current State of Global Commodity Markets
The commodity markets present an intriguing landscape in 2025. Market projections indicate that 59% of the most valuable and liquid commodities will trade below their 2024 levels. Several interconnected factors have shaped this market reality.
Key Commodity Price Trends
Different sectors in the commodities market display varied performance patterns. Gold and silver have reached remarkable heights—gold touched USD 2,790.00 per ounce while silver hit a 12-year high at USD 35.00 per ounce. The outlook hasn’t been as promising for coal, lithium, and soybeans, which ended lower.
Natural gas markets experienced significant price volatility. The U.S. benchmark Henry Hub Natural Gas Spot Price reached its lowest inflation-adjusted yearly average at USD 2.21 per MMBtu in 2024. Brent crude oil futures maintained relative stability, with an average of USD 80.00 per barrel.

Major Market Drivers in 2025
Several crucial factors are shaping commodity markets this year:
Global Economic Growth: The International Energy Agency has adjusted its global oil-demand growth forecast to 1.1 million barrels per day, largely due to China’s recent stimulus measures.
Supply Dynamics: Oil markets may experience surpluses in early 2025 as new production flows in from the United States, Canada, Guyana, and Brazil. Global supply is expected to exceed demand by 950,000 barrels per day.
Currency Effects: The dollar’s strength continues to influence commodity prices, making dollar-based assets more expensive for international buyers.
Regional Market Differences
Market disparities across regions have become increasingly pronounced. China’s economic challenges significantly impact metal markets since the country consumes more than half of the world’s metals. The U.S. market’s import dependence is notable—it consumes 4.7 million tons of primary aluminum but produces only 0.7 million tons domestically.
Europe faces unique challenges after banning Russian pipeline imports at the end of 2024. This policy shift has pushed Europe to increase its reliance on U.S. LNG exports as new Gulf of Mexico capacity becomes operational.
Agricultural markets display distinct regional patterns. Brazil exports coffee at record levels despite poor harvests. West African cocoa production struggles with drier weather, resulting in reduced deliveries at Côte d’Ivoire ports.
These regional variations highlight the complex interaction between local conditions and global trends, creating unique challenges for economies heavily dependent on commodities, particularly in emerging markets and developing nations.
Direct Effects of Geopolitical Events
Global events have fundamentally transformed commodity market dynamics, leading to unforeseen supply chain disruptions and price volatility. Market turbulence primarily stems from uncertainty shocks, especially in regions rich with energy and mineral resources.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The ‘global value chain’ model that served the world economy effectively for thirty years now faces significant challenges. Companies must reassess their global network designs as geopolitical disputes trigger supply chain complications.
Supply chain issues have most severely impacted the automotive, pharmaceutical, food, and healthcare sectors. For example, sanctions disrupted operations in Europe’s gas-dependent industries, including:
- Chemicals manufacturing
- Steel production
- Cement and glass manufacturing
- Paper and printing operations

The complexity of modern supply chains necessitates reliable, comparable, and real-time information through multiple layers of customers and suppliers. Military conflicts and extreme weather events created additional challenges for global commerce in late 2023, forcing shipping companies to identify alternative routes.
Price Volatility Patterns
Different commodities respond to geopolitical pressures in unique ways. Recent studies indicate that geopolitical risk:
- Increases volatility in coal, iron ore, and crude oil futures prices
- Reduces gold price volatility
- Shows no significant effect on copper futures
Commodities with greater dependence on external factors demonstrate stronger volatility responses. European natural gas markets surged by 7.5% during geopolitical events, while US and Asian markets remained relatively stable.
Agricultural markets exhibit their own vulnerability patterns. Wheat prices typically rise 2% and corn prices increase 1% during major geopolitical events. Wheat prices continue to feel the effects for approximately 70 days after the initial shock.
Several factors determine how commodity markets react to geopolitical tensions:
- The degree of market financialization
- Commodity storability
- Transportation convenience
- Supply flexibility
- Weather condition dependence
Commodity traders anticipate continued price volatility throughout 2025. This outlook stems from supply and demand risks, along with supply chain transformations driven by electric mobility and renewable energy adoption. The renewable energy expansion introduces additional trading challenges due to the inherently greater price volatility of renewable electricity.
These disruptions extend beyond price effects. Supply chain problems can spread to third-party countries when restrictions are imposed, causing shortages of essential resources and affecting industrial production worldwide. Periods of increased geopolitical tension frequently result in higher inflation, slower growth, and significant welfare losses.
How Different Commodities React
Commodities respond differently to geopolitical pressures, creating unique market dynamics across various sectors. Market participants must understand these patterns to navigate the complex 2025 market landscape effectively.
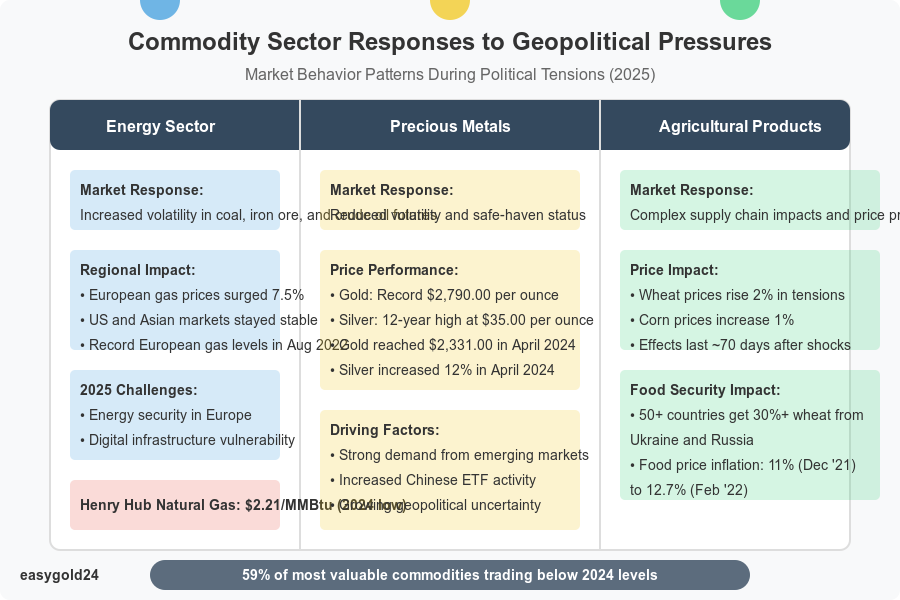
Energy Sector Response
Energy security remains Europe’s most significant challenge in 2025, particularly after losing Russian gas supplies. The increasing digitization of modern energy infrastructure has created new vulnerabilities. The sector faces potential disruptions from cyberattacks that could affect critical supply chains.
Regional factors heavily influence natural gas markets. European gas prices reached record levels in August 2022 due to supply uncertainties. This situation prompted many countries to restart their conventional coal plants, temporarily reversing progress toward clean energy goals.
Precious Metals Behavior
Gold continues to prove its value as a reliable safe-haven asset that maintains stability during market turmoil. Gold prices reached a new nominal record of USD 2,331.00 per troy ounce in April 2024. Three primary factors drove this surge:
- Strong demand from emerging market central banks
- Increased activity from Chinese exchange-traded funds
- Growing geopolitical uncertainty
Silver’s value increased significantly with a 12% rise in April 2024, driven by industrial activity recovery and gold market influences. Platinum demonstrated strength by rising 3.5% after a slight decline in early 2024.
Studies confirm that precious metals serve as effective hedges against political uncertainty. Gold markets remain stable even during periods of unexpected economic policy changes. This characteristic makes precious metals excellent portfolio diversification tools when markets become unstable.
Agricultural Products Impact
Geopolitical tensions create complex challenges for the agricultural sector. Global production of crops, livestock, and aquaculture commodities grew from USD 1.10 trillion to USD 4.30 trillion between 1961 and 2024. Recent global events have introduced additional market pressures.
Food security has become a critical concern as higher prices drive inflation rates upward worldwide. More than 50 countries obtain over 30% of their wheat from Ukraine and Russia. Fifteen nations depend on these suppliers for more than 70% of their imports. This reliance caused widespread economic effects:
- Food price inflation reached 11% in December 2021
- Rose to 11.9% in January 2022
- Increased to 12.7% in February 2022
Agriculture demonstrates varying levels of resilience. Global agricultural output grew at an annual rate of 2.3% from 1961 to 2020 but slowed to 1.93% between 2011 and 2020. Improved farming methods have reduced resource requirements. The cropland needed to produce USD 1,000.00 of commodities decreased from 1.1 hectares to 0.6 hectares between 1990 and 2020.
Hidden Market Transmission Channels
Geopolitical events extend beyond direct market disruptions. They initiate subtle yet powerful chain reactions that transform commodity markets by altering currency values and trade patterns. These hidden forces often amplify the original market shocks and leave lasting impacts on the global economy.
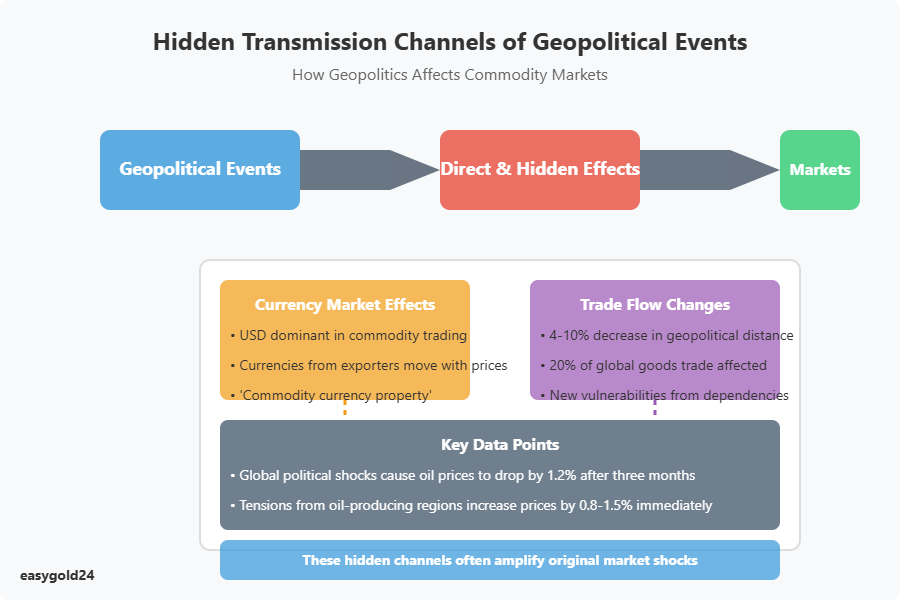
Currency Market Effects
The U.S. dollar’s position as the dominant currency in global commodity trading creates complex ripple effects during periods of geopolitical tension. Since commodities trade primarily in dollars, currency fluctuations can dramatically affect purchasing power and trade dynamics. For instance, a stronger dollar diminishes the value of other currencies, complicating global trade relationships.
Different regions exhibit unique relationships between commodities and currencies:
- The South African rand correlates closely with precious metals prices due to South Africa’s significant export position
- The Chinese renminbi’s value against the dollar substantially affects copper markets since China dominates global copper trading
- Fluctuations in the Mexican peso influence corn imports because Mexico is the largest purchaser of U.S. corn
Research demonstrates that currencies from commodity-exporting countries move synchronously with global commodity prices. This “commodity currency property” means higher commodity prices typically strengthen these currencies through improved trade terms.
Commodity market uncertainty increases the sensitivity of commodity-producing economies’ exchange rates to changes in commodity trade terms. Data indicates that global commodity price uncertainty initially depresses commodity currencies, which subsequently recover in the medium term.
Trade Flow Changes
Geopolitical tensions are reshaping long-established trade patterns. Since 2017, major economies have reduced trading with geopolitically distant partners. China, Germany, the United Kingdom, and the United States have each decreased their geopolitical trade distance by 4% to 10%.
Trade between countries with limited political alignment now constitutes:
- Almost 20% of global goods trade
- Approximately 40% of trade in globally concentrated products
These trade flow transformations present significant challenges. Investment trends illustrate this shift—new investments in China and Russia declined by 70% and 98% compared to pre-pandemic levels. Meanwhile, Africa and India experienced the most substantial investment increases over the past two years.
These shifts create new vulnerabilities. Some countries have developed excessive dependence on politically distant partners for critical imports or exports. Germany’s reliance on Russian energy necessitated major trade adjustments following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
The future presents two potential paths for trade relationships. Countries will either redirect trade toward politically friendly partners, increasing trade concentration by 13%, or diversify their trade to reduce dependency, accepting a 3% increase in political distance.
Risk Management Strategies
Risk management sophistication plays a crucial role in commodity trading success for 2025 as global events continue to shape market dynamics. Recent data indicates that geopolitical risks strengthen connections between commodity markets, with concrete actions creating more significant changes than threats in these markets.
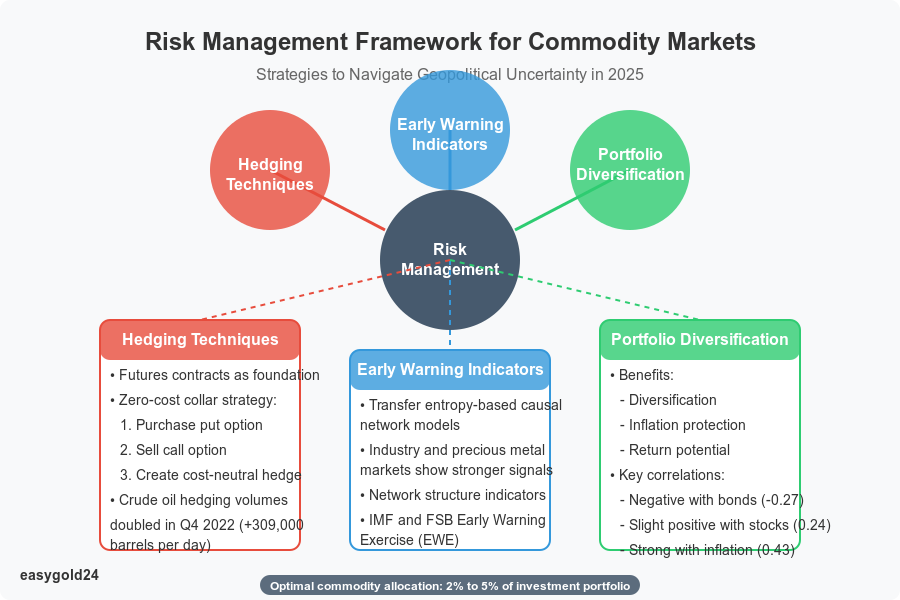
Early Warning Indicators
Transfer entropy-based causal network models provide effective early warning signals about systemic risk in commodity markets. These indicators function optimally when problems develop gradually rather than emerging suddenly.
Key early warning signals include:
- Industry and precious metal markets demonstrating stronger information transmission capabilities
- Network structure indicators providing warnings about systemic risk
- Sentiment indicators revealing gradual but notable declines before major market changes
The IMF and Financial Stability Board’s Early Warning Exercise (EWE) evaluates low-probability but high-impact risks, helping to identify vulnerabilities before they trigger systemic shocks.
Hedging Techniques
Futures contracts serve as the foundation of hedging tools, providing predetermined prices for specific commodities at future dates. Options strategies offer compelling alternatives, particularly zero-cost collars that eliminate premium costs while protecting investments.
A zero-cost collar strategy operates as follows:
- Purchase a put option for downside protection
- Sell a call option to offset the put option’s cost
- Create a cost-neutral hedge with defined price ranges
Crude oil hedging volumes nearly doubled in Q4 2022, with an additional 309,000 barrels per day. Gas producers implemented over 4.02 billion cubic feet per day in new hedges.
Portfolio Diversification Approaches
Investment portfolios benefit from commodities in three primary ways: diversification, inflation protection, and return potential. Long-term data demonstrates that commodities maintain a negative correlation with bonds (-0.27) and a slight positive correlation with stocks (0.24).
Portfolio optimization research reveals:
- Commodities exhibit a 0.43 correlation with inflation
- A 2% to 5% allocation is sufficient to create meaningful portfolio effects
- Commodity price fluctuations generate buy-low and sell-high opportunities through rebalancing
Different inflationary and economic conditions influence the optimal allocation percentage. Commodities prove particularly valuable in the current environment due to their structural connection to inflation, consistent correlation direction, and significant beta magnitude.
Market history offers an important insight about commodities following recessions. Limited spare capacity and investment before economic downturns typically lead to supply constraints once demand recovers. Astute investors may view mild recession-related weaknesses as opportunities to establish inflation protection.
The Role of Geopolitical Events in Shaping Commodity Prices
Geopolitical events are powerful drivers in the commodity markets, influencing prices and supply chains in complex ways. For example, the invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 led to a nearly 30% increase in Brent oil prices in just two weeks, highlighting the immediate impact of political shocks on energy markets. While it’s commonly believed that such events lead to higher commodity prices, the reality is more nuanced. Data shows that while geopolitical tensions generally cause oil prices to drop by 1.2% over three months, tensions in key oil-producing regions typically lead to immediate price increases of 0.8% to 1.5%.
Preparing for Future Market Shifts in 2025
In 2025, new geopolitical challenges are expected to continue shaping commodity markets, with disruptions ranging from energy to precious metals and agricultural products. Supply chain disruptions and price fluctuations driven by political events create both risks and opportunities for traders and businesses.
Strategic Insights for Effective Risk Management
Understanding the intricate relationships between geopolitics and commodity prices is essential for developing effective risk management strategies. The ability to anticipate market shifts based on both obvious and hidden signals can provide a significant advantage in the unpredictable world of commodity trading.
As Hartmann & Benz continues to grow and prepare for its public listing on the OTCQB market, the company is positioning itself to respond effectively to these global shifts. By offering shares and a security token backed by gold, Hartmann & Benz is helping investors access opportunities in a market that’s deeply connected to geopolitical events. Keep up with our progress and stay informed about the upcoming developments in the global commodities market.

