GOLD TRADING
How to Trade Gold in 2025
Gold trading has become a cornerstone of financial markets. Central banks now hold approximately 37,755 metric tons of gold, representing about 17-20% of all gold ever mined.
The COVID-19 crisis demonstrated gold’s effectiveness as a safe-haven asset when prices increased by 13% between January and May 2020. Currently trading at $2,935.81 per ounce, with jewelry accounting for 50% of global consumption, gold trading remains more relevant than ever.
You can trade gold through various instruments including CFDs, futures contracts, or ETFs. Learn about the essentials of gold trading, understand market fundamentals and prepare to place your first trade with confidence.
What is Gold Trading
Gold trading has evolved significantly beyond simply purchasing physical gold. The precious metal stands out as a versatile financial asset that provides traders with multiple options based on their objectives and risk tolerance.
Physical Gold vs Digital Trading : Purchasing physical gold involves acquiring actual gold jewelry, coins, or bars. This traditional approach allows you to own tangible assets and eliminates counterparty risk. However, it comes with additional considerations. You must pay for storage and insurance, and there’s always the risk of theft. For these reasons, physical gold is better suited for long-term investment strategies.
Digital trading enables you to profit from gold’s price movements without possessing the actual metal. Traders can participate in the XAU/USD market through Contract for Differences (CFDs), which ranks among the most traded pairs. This approach requires less initial capital and offers greater flexibility than owning physical gold.
Digital Gold Tokens : Digital gold tokens represent an innovative approach to gold investment. Each token is backed by physical gold stored in secure vaults. These tokens offer several advantages over traditional gold ownership:
- Improved Accessibility: You can purchase smaller gold quantities than would be practical with physical gold
- Transparent Verification: Blockchain technology provides permanent ownership records that anyone can verify
- Reduced Expenses: Smart contracts help streamline processes and reduce settlement fees
Each digital gold unit is backed by 24K 99.9% pure gold and trades at current market prices. However, it’s important to note that digital platforms typically charge 2-3% for management, storage, and insurance of your gold.
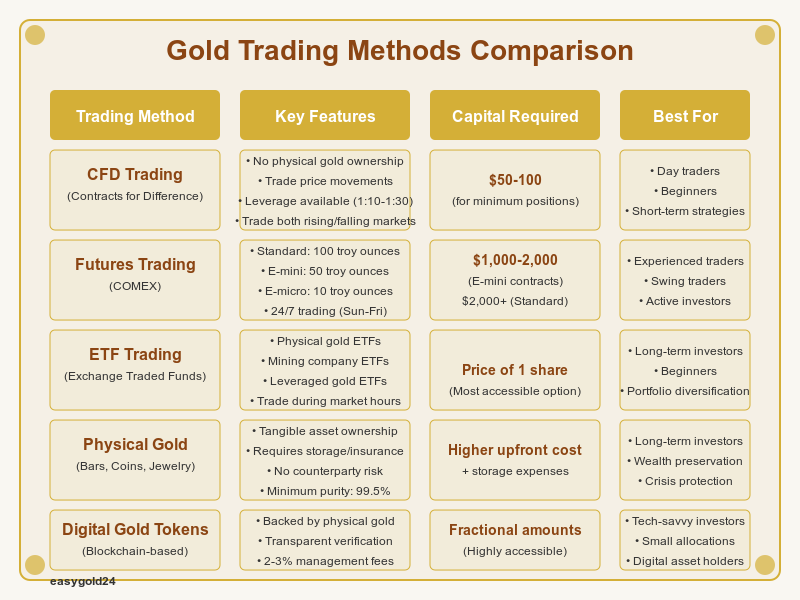
Different Ways to Trade Gold :
The gold market offers several trading methods:
- Futures Trading: These contracts allow two parties to agree on future gold transactions. Each contract typically represents 100 troy ounces of gold futures.
- Options Trading: Gold options require lower initial investment and provide more strategic flexibility. You can trade these contracts on exchanges like COMEX to speculate on gold price movements.
- Spot Trading: This involves buying and selling gold immediately through banks or trading platforms. You can quickly adjust your strategy as market conditions change.
- ETF Trading: Gold Exchange-Traded Funds combine various gold stocks and securities, offering a diversified approach to investing in the gold sector.
- Mining Stocks: You can gain exposure to gold’s potential by investing in mining companies. Your returns depend on both gold prices and company performance.
With these diverse options, you can select the approach that best aligns with your investment goals, risk tolerance, and desired level of market involvement.
Gold bars feature lower premiums than coins, making them more cost-effective for substantial investments. The premium structure varies by size:
According to recent market analysis, investors can save up to 5-7% on premiums when purchasing gold bars versus comparable gold coins.
Gold Market Fundamentals
Gold’s market value depends on supply and demand dynamics, with mining production growing at just 1.6% annually. This limited supply helps gold maintain its role as a store of wealth for over three thousand years.
Supply and Demand Basics :
Gold distinguishes itself from other precious metals due to its scarcity – it’s six times rarer than platinum and 18 times rarer than silver. The production costs for North American miners have doubled since 2008, illustrating how expensive mining has become.
The gold market demonstrates impressive diversity across different sectors:
- Investment Demand: ETF investments began 2025 strongly, with Europe leading inflows and reaching the highest levels since March 2022
- Central Bank Activity: Banks remained major buyers, and their purchasing patterns indicate continued upward price pressure
- Consumer Markets: Asian investors, particularly in India and China, continue to show steady interest
- Industrial Usage: Technology applications create consistent demand
This diverse demand structure creates a self-balancing market mechanism that strengthens gold’s position as an investment asset.
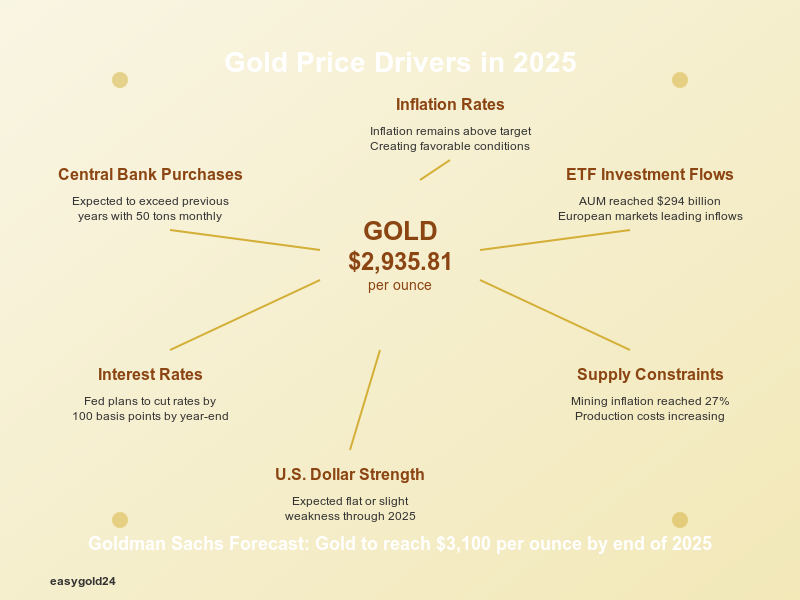
Price Drivers in 2025 : Gold prices in 2025 are being influenced by several significant factors:
Gold’s price trajectory over the past two decades reveals a compelling story of resilience and growth. Since its modest valuation of USD 274.5 per ounce in 2000, gold has shown remarkable appreciation, particularly during periods of economic uncertainty.
- Central Bank Purchasing: Banks have maintained their gold-buying momentum, and demand is projected to exceed previous years.
- Economic Indicators: The Federal Reserve plans to cut rates by 100 basis points by year-end, while inflation remains above target – creating favorable conditions for gold. The U.S. dollar’s expected flat or slight weakness through 2025 could benefit gold prices.
- Market Volatility Factors: Goldman Sachs expects gold to reach USD 3,100 per ounce by the end of 2025. This forecast is based on:
- Monthly central bank demand of 50 tons
- Rising ETF holdings as interest rates fall
- A potential increase to USD 3,300 if policy uncertainty continues
Supply Constraints: Mining faces several challenges:
- South Africa’s output has decreased by half over the last several years
- Global mining inflation reached 27% last year
- Rising production costs establish higher price floors
Investment Flows: ETF investments have demonstrated impressive strength:
- Total assets under management reached USD 294 billion
- European markets lead with significant inflows
- Market uncertainties drive growing institutional interest
These fundamentals become increasingly important as gold attracts diverse market participants. Supply constraints combined with varied demand create a complex yet promising trading environment. With ongoing geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainties, gold’s outlook remains strong through 2025.
Required Starting Capital
The capital needed to begin gold trading depends on your preferred trading method:
Current market conditions for gold price forecast
Physical Gold Investment: Many traditional investors prefer physical gold. You should acquire gold that’s at least 99.5% pure, but remember to budget for storage and insurance costs.
Digital Trading Options: Digital platforms require less initial capital:
- CFD Trading: Approximately USD 50-100 for minimum positions
- E-Mini Contracts: USD 1,000-2,000 allows you to begin futures trading
- Standard Futures: USD 2,000 for a minimum position of 0.001 lots (100 ounces)
Portfolio Allocation Strategies: Financial experts recommend allocating 10% to 20% of your investment portfolio to gold for inflation protection. Your initial capital should align with your investment strategy and risk tolerance.
Cost Considerations Beyond Starting Capital
Storage Costs:
- Bank safety deposit boxes
- Professional vault facilities
- Insurance coverage
Transaction Fees:
- Dealer markups above spot price
- Management fees for digital platforms
- Trading commissions
Each investment type requires different amounts of capital:
- Gold ETFs: The most accessible option – purchase a single share
- Mining Stocks: Available through stock market brokers at various price points
- Physical Bullion: Higher upfront costs plus storage expenses
- Gold IRAs: Suitable for retirement planning with specific minimum requirements
The Federal Reserve’s policy changes have created an ideal environment for gold investment. Analysts predict approximately 100 basis points in rate cuts throughout 2025, which could enhance gold’s attractiveness as an investment option.
Leverage Considerations
Leverage means you need less initial capital, but risks increase:
- Stock brokers offer up to 1:20 leverage
- Forex platforms may provide higher ratios
- Position sizing becomes crucial with leverage
Starting Small vs. Optimal Capital
Some platforms allow you to begin with just USD 10.
New traders should start with USD 1,000-2,000 to balance accessibility and effectiveness. This amount helps you properly size positions and navigate market fluctuations.
Understanding Gold Markets
The gold market processes over USD 200 billion in daily transactions, making it one of the most actively traded commodities worldwide. Understanding how gold markets function is essential for trading success.
Spot Gold Prices
Spot gold represents the current purchase price for immediate delivery of physical gold. Buyers and sellers negotiate directly through over-the-counter trading to establish prices. The London Bullion Market Association (LBMA) sets the standard through electronic auctions that include 13 member banks, including Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, and Bank of China.
The spot price flows through the supply chain in this manner:
- Miners sell to refineries slightly below spot.
- Refiners sell to mints just above spot.
- Mints create product and sell it to dealers at competitive prices.
- Dealers add small margins for retail sales.
Gold Futures Markets
Modern gold trading operates primarily through futures contracts. More than 90% of COMEX contracts are settled without physical metal changing hands. These standard agreements include:
- Contract Size: Standard contracts are 100 troy ounces, with smaller e-mini (50 ounces) and e-micro (10 ounces) options
- Trading Hours: Markets operate from 6 PM EST to 5 PM EST Sunday through Friday, with peak trading occurring between 6 AM and 10 AM EST
- Price Movement: A 10-cent change in gold price translates to a USD 10 value change per contract
Spot and futures prices are connected through precise financial calculations. Futures prices typically exceed spot prices (contango) due to current interest rates. Occasionally, spot prices rise above futures prices (backwardation), usually during market stress periods.
Gold ETFs Explained
Gold Exchange-Traded Funds allow investors to gain exposure to gold without owning physical metal. These investment vehicles offer distinct benefits:
Physical Gold ETFs:
- Track gold prices directly through bullion holdings
- Eliminate storage and security concerns
- Provide better liquidity than physical gold
- Allow investors to start with smaller amounts
Mining Company ETFs:
- Focus on companies with gold mining operations
- Link performance to gold prices and company efficiency
- Provide indirect exposure to gold market movements
Leveraged Gold ETFs:
- Utilize derivatives to amplify returns
- Are best suited for experienced investors
Gold ETFs have specific tax implications. Long-term investments are subject to a 28% tax rate instead of the standard 20% capital gains. Nevertheless, investors continue to choose them for their convenience and trading efficiency.
Basic Gold Trading Tools
Gold traders must develop proficiency with technical tools that analyze market movements and identify trading opportunities. These tools are essential for making informed trading decisions in the dynamic gold market.
Essential Price Charts
- Identify support areas for buying opportunities
- Recognize resistance levels for selling opportunities
- Observe trends across various time periods
Gold price charts display data in multiple weight measurements – grams, ounces, and kilograms. Traders can analyze price movements based on their preferred trading units. For example, individual investors often examine gram-denominated charts, while institutional traders monitor prices in ounces or kilograms.
The gold/silver ratio chart serves as another valuable analytical tool. This ratio is calculated by dividing gold’s price by silver’s price. For instance, if gold costs USD 120,000 per ounce and silver costs USD 15.00 per ounce, the ratio would be 80, indicating that it requires 80 ounces of silver to purchase one ounce of gold.
Key Trading Indicators
Technical indicators help traders interpret market conditions and identify potential entry and exit points. Here are the most reliable indicators for gold trading:
Moving Averages (MA): Moving averages smooth out price fluctuations and highlight trends. Traders commonly use:
- 50-day and 200-day moving averages to identify trends
- Golden cross (short-term MA crossing above long-term MA) signals bullish movements
- Death cross (short-term MA crossing below long-term MA) signals bearish movements
Relative Strength Index (RSI): RSI measures momentum and identifies market extremes:
- Readings above 70 indicate overbought conditions
- Values below 30 suggest oversold situations
- Regular touches of 70 during uptrends confirm strong momentum
Bollinger Bands: These bands expand and contract with market volatility, helping traders:
- Identify potential breakouts
- Assess current market volatility
- Select better entry and exit points
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): MACD combines trend following and momentum:
- Measures the distance between 12-day and 26-day moving averages
- Buy signals occur when MACD line crosses above signal line
- Sell signals appear during bearish crossovers
Fibonacci Retracement: This tool identifies potential support and resistance levels using mathematical sequences:
- Locates entry points during corrections
- Predicts possible reversals during pullbacks
- Functions most effectively in strong gold market trends
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) publishes weekly Commitments of Traders reports, which explain market positions among hedge funds and money managers. The Daily Sentiment Index (DSI) complements technical indicators by assessing market sentiment through the percentage of traders taking long versus short positions.
How to Place Your First Gold Trade
Your first gold trade requires careful consideration of different trading methods and adherence to a structured approach. The following information will help you begin your gold trading journey.
Selecting Your Trading Method
Beginners typically find CFDs or ETFs the most straightforward way to trade gold. These instruments offer several advantages:
- Lower capital requirements
- No physical gold storage needed
- Profit potential in both rising and falling markets
- Various leverage options available
Gold CFDs allow you to trade based on the difference between opening and closing prices. Trading platforms provide:
- Advanced charting capabilities
- Customizable indicators
- Automated trading features
Step-by-Step Trading Process
Complete these fundamental steps before your first trade
- Select a broker offering gold trading instruments
- Verify they are regulated by reputable authorities
- Evaluate their trading platforms and tools
Account Setup:
- Complete verification procedures
- Submit identification documents
- Deposit your initial capital
Platform Familiarization:
- Utilize demo accounts
- Familiarize yourself with platform tools
- Learn about different order types and execution methods
Trade Execution:
- Select your gold trading instrument
- Determine your position size
- Set your entry price and order type
- Establish stop-loss and take-profit orders
Managing Your Position
Effective position management is crucial for successful gold trading. Consider these proven strategies:
Risk Management Guidelines:
- Limit risk to 1-2% of your account value per trade
- Calculate precise lot sizes using position calculators
- Place stop-losses at technical levels
Take Profit Strategies:
- Target realistic profits using support/resistance levels
- Consider implementing trailing stops
- Secure profits when trades move favorably
Leverage Considerations: Your broker may offer leverage ratios from 1:10 to 1:30. New traders should:
- Begin with lower leverage
- Increase leverage gradually as they gain experience
- Maintain adequate margin reserves
Active Position Monitoring: Futures positions require careful attention due to:
- Leverage effects on trades
- Margin requirements
- Contract expiration dates
Exit Strategies: Develop clear plans to exit based on:
- Technical analysis points
- Fundamental market changes
- Risk-reward considerations
- Contract rollovers near expiration
Remember that emotional decisions can be costly. A well-structured approach with predetermined entry and exit points helps avoid bias and promote consistent trading. As you gain experience, you can adjust position sizes and risk levels while adhering to your trading plan.
Common Gold Trading Strategies
Gold traders employ various strategies to capitalize on price movements across different market timeframes. Understanding these approaches helps you select the most suitable method for aligning your trading objectives with market conditions.
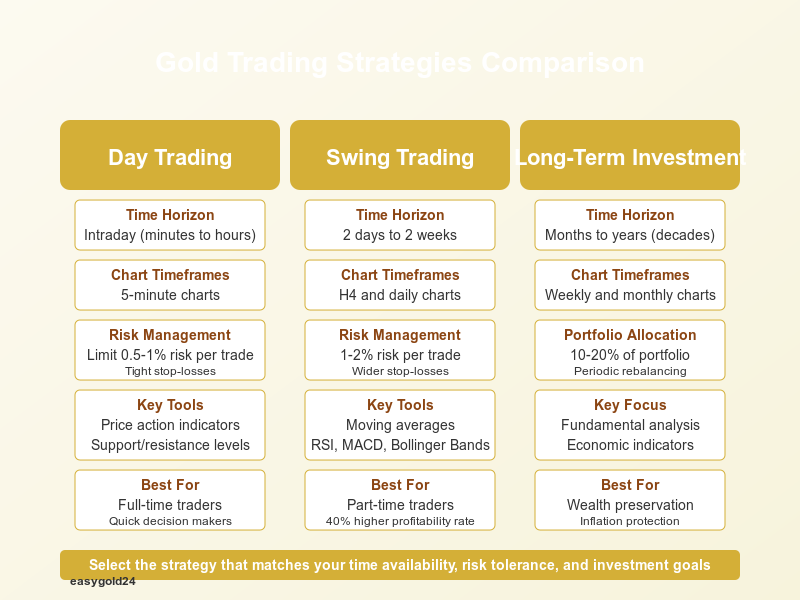
Day Trading Gold
Day traders execute multiple trades within a single session, profiting from short-term price fluctuations. This strategy is most effective using 5-minute chart timeframes for entry and exit points.
Successful day traders focus on these critical elements:
- Market Analysis: They monitor upcoming news events and trends affecting intraday volatility
- Position Management: They implement stop-loss orders and practice effective capital management
- Technical Tools: They utilize price action indicators and support/resistance levels
- Risk Control: They limit exposure to 0.5-1% per trade to preserve capital
Swing Trading Approach
Swing trading gold represents a middle ground between day trading and long-term investing, with positions held from two days to two weeks. This strategy offers several advantages:
Time Management Benefits:
- Reduced screen time requirements
- Lower stress from fewer immediate decisions
- More time for thorough setup analysis
Market Analysis Framework:
- Higher timeframes indicate overall trends
- H4 charts help determine precise entry points
- Technical indicators confirm trade decisions
Studies indicate swing traders achieve 40% higher profitability than day traders because they:
- Capture larger price movements
- Incur fewer transaction costs
- Make less emotionally-driven trading decisions
Long-Term Investment Strategy
Long-term gold investors focus on fundamental factors rather than daily price movements. This strategy values gold’s unique characteristics:
Portfolio Benefits:
- Preserves value without credit risk
- Enhances portfolio diversification with low correlation to stocks and bonds
- Provides protection against inflation and currency devaluation
Investment Allocation: Financial experts recommend allocating 10-20% of investment portfolios to gold. This allocation helps:
- Provide protection during market volatility
- Maintain liquidity during market stress periods
- Preserve value over extended timeframes
Market Positioning: Major institutional investors like pension funds and foundations often hold physical gold for decades. They typically:
- Rebalance portfolios periodically
- Monitor fundamental price drivers
- Disregard short-term market fluctuations
2025 Market Outlook: Goldman Sachs projects gold reaching USD 3,100-3,200 by year-end, based on:
- Lower cash rates stimulating retail investment
- Continued strong central bank purchases
- Potential increases in ETF holdings
Each strategy requires different skills, time commitments, and risk management approaches. Day traders must constantly monitor markets and make rapid decisions. Swing traders enjoy more flexible schedules with reduced stress. Long-term investors concentrate on fundamentals and maintain their positions through market cycles.
Managing Trading Risks
Risk management is essential for successful gold trading and determines long-term profitability in volatile markets. Traders who effectively implement stop-losses and properly size their positions protect their trading capital while maximizing potential returns.
Setting Stop Losses
Stop-loss orders are crucial risk management tools that automatically close trades at predetermined levels. These orders prevent excessive losses and help traders maintain discipline.
Types of Stop-Loss Orders:
- Fixed Stop Loss: Established at specific price points below entry for long positions or above entry for short positions. For example, purchasing gold at USD 1,800 per ounce might require a stop loss at USD 1,770 to limit potential losses.
- Trailing Stop Loss: The stop-loss level adjusts upward as prices move favorably to secure profits while maintaining downside protection. This preserves gains as gold prices appreciate.
- Volatility-Based Stop Loss: Market conditions determine stop levels using indicators like Average True Range (ATR) to ensure stops aren’t excessively tight or loose.
Best Practices for Stop-Loss Implementation:
- Use technical analysis to guide stop placement
- Ensure adequate distance between entry points and stops
- Consider market volatility when determining stop levels
- Maintain risk-to-reward ratios of at least 1:2
Traders who neglect to use stop losses often retain losing positions too long, hoping for market reversals. This “hope strategy” frequently results in deeper losses, highlighting the importance of predetermined exit points.
Gold Exchange-Traded Funds allow investors to gain exposure to gold without owning physical metal. These investment vehicles offer distinct benefits:
Position Sizing Basics
Position sizing determines trade units relative to account capital and significantly impacts risk management outcomes. Professional traders typically risk 1-2% of their account value per trade.
Position Size Calculation Method:
Follow these steps to calculate position sizes:
- Define your risk amount per trade
- Identify your entry point
- Determine your stop-loss level
- Apply this formula: Position Size = Risk Amount / (Price Difference × 100)
For example, with a USD 100,000 account risking 0.6% per trade (USD 600) and a stop loss 6.92 points away, the calculation yields 0.867 lots. This should be rounded down to 0.86 lots to remain within risk parameters.
Risk Management Framework:
Effective position sizing considers multiple factors:
- Account size considerations
- Market volatility assessment
- Risk tolerance evaluation
- Trading strategy requirements
Diversification enhances risk management by distributing investments across different assets, including:
- Multiple forms of gold investment
- Various precious metals
- Stocks and bonds
- Real estate allocations
Take-Profit Strategies:
Take-profit orders complement stop losses to secure gains. For instance, a gold purchase at USD 1,800 might have a take-profit set at USD 1,830 to capture profit before potential market reversals.
Advanced Risk Control Measures:
- Regular position exposure monitoring
- Position size adjustments based on changing market conditions
- Proper margin requirement maintenance
- Trade documentation in performance journals
Institutional investors like pension funds and foundations demonstrate the value of proper position sizing through their methodical approach to gold allocation. Their strategy involves systematic portfolio rebalancing and emphasis on fundamental price drivers rather than short-term fluctuations.
Trading Gold with Market News
Gold traders must understand market dynamics and economic indicators that influence precious metal prices. Careful analysis of market data and events helps identify profitable opportunities and improve risk management.
Reading Economic Data
Gold prices respond to these key economic indicators:
- Inflation Data: Gold prices followed an unexpected trajectory as inflation rose in 2022. They initially declined but subsequently recovered to reach new highs in 2024. This demonstrates gold’s function as a hedge against currency devaluation.
- Interest Rates: Real yields represent the most significant factor influencing gold price movements. The anticipated interest rate reductions of 100 basis points by year-end create ideal conditions for gold price appreciation.
- Employment Reports: Weekly jobless claims can trigger rapid price adjustments. Experienced traders monitor these statistics carefully. Any unexpected changes can prompt immediate market reactions.
Using News Events
News-based trading is most effective with a systematic approach to analyzing different event types:
- Economic Uncertainty: Market volatility, currency fluctuations, and inflation rates can trigger price movements. Traders look for unusual patterns in these metrics. When anomalies are detected, gold prices often adjust shortly thereafter.
- Supply Factors: Mining issues now affect gold prices more substantially than ever before. Gold extraction has become more expensive due to rising costs and environmental regulations. Unexpected disruptions such as strikes or natural disasters can drive prices higher.
- Market Sentiment: The Daily Sentiment Index reflects trader sentiment by tracking long versus short positions. Institutional investors combine this data with technical analysis to optimize trade timing.
- Trading Considerations: Gold prices typically rise before conflicts but stabilize or decline once hostilities commence. This follows the classic “buy the rumor, sell the news” pattern observed in financial markets.
Currently, gold functions as a barometer of U.S. economic confidence. Its price increases when faith in the economy diminishes. This helps traders contextualize news events within broader market trends.
Conclusion
Gold trading offers exceptional opportunities for investors who understand market fundamentals and implement appropriate strategies. Traders can participate in this USD 200 billion daily market by analyzing price drivers, technical indicators, and risk management techniques.
Successful trading requires essential tools and comprehensive knowledge of market influences. Gold prices fluctuate significantly based on central bank activities, economic indicators, and geopolitical events. The most effective traders integrate these fundamental factors with technical analysis to achieve optimal results.
Risk management is vital for profitable gold trading. Proper position sizing, strategic stop-loss placement, and disciplined trade execution protect capital while maximizing potential returns. Novice traders should begin with smaller positions to gain experience without excessive risk exposure.
Gold’s enduring value has persisted for three millennia, making it a unique asset for both short-term trading and long-term investment. The knowledge provided in this guide will help you confidently begin your gold trading journey while maintaining realistic expectations and implementing appropriate risk controls.
