Stock Analysis
Stock Analysis Strategies for Smarter Investing in 2025
Navigating today’s markets requires more than instinct. A well-structured approach to stock analysis empowers you to act with clarity and confidence — whether Sie just getting started or refining an existing strategy.
Understanding key fundamentals such as valuation metrics, technical indicators, and sector-specific performance is essential for identifying promising opportunities. Tools like price-to-earnings ratios, cash flow analysis, and return on equity help uncover companies with strong potential and sound financials.
The integration of AI and advanced analytics has redefined what’s possible. Real-time data, algorithmic models, and automated screening solutions allow Sie to detect patterns, manage risk, and respond faster to shifting market dynamics — without sacrificing precision.
A solid analysis process also includes macroeconomic insights, competitive positioning, and company-specific risk factors. Combining technical and fundamental perspectives provides a more complete view and supports better decision-making.
Use these methods to sharpen your strategy and uncover opportunities with real value. Stay informed. Act strategically. Invest with purpose.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Stock Analysis
Stock analysis forms the foundation of intelligent investing decisions in the ever-evolving financial markets. At its core, stock analysis involves evaluating securities to determine their intrinsic value, growth potential, and risk factors. Investors employ various methodologies to assess stocks, with fundamental and technical analysis being the primary approaches used by market participants worldwide.
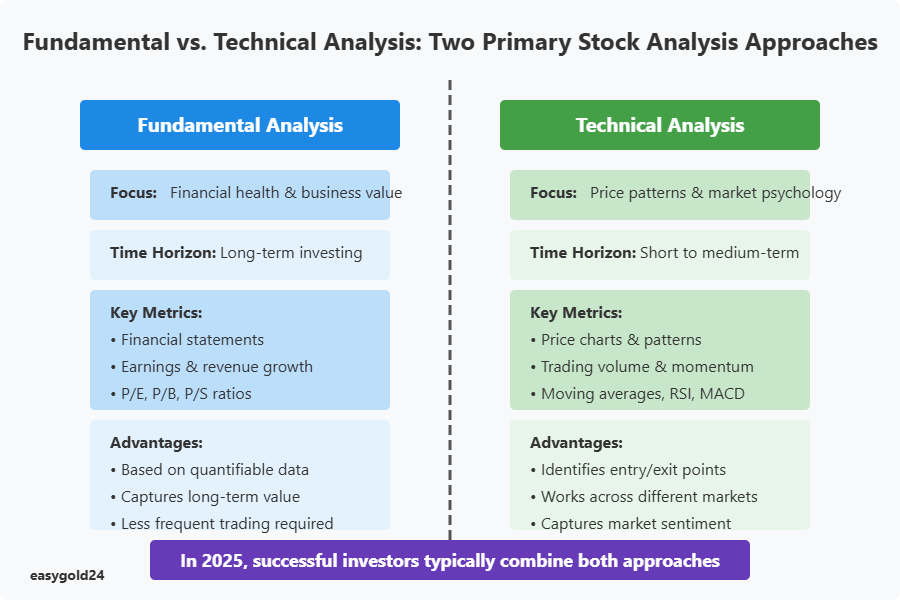
Fundamental analysis examines a company’s financial health, business model, competitive positioning, and macroeconomic environment to determine its intrinsic value. This approach focuses on financial statements, earnings reports, industry trends, and management quality to identify undervalued or overvalued securities. By contrast, technical analysis studies historical price movements and trading volumes to predict future market behavior, using charts, patterns, and statistical indicators to identify entry and exit points.
In 2025’s market environment, successful investors typically combine both fundamental and technical methodologies for a comprehensive analytical framework. This integrated approach provides a more complete picture of a stock’s potential, allowing investors to make decisions based on both quantifiable financial metrics and market sentiment indicators. As markets become increasingly efficient, the ability to synthesize multiple analytical perspectives has become crucial for identifying genuine investment opportunities.
Fundamental Analysis: Evaluating Company Health
Fundamental analysis serves as the cornerstone of long-term investment strategies, focusing on comprehensive evaluation of a company’s financial health and business prospects. This methodology involves scrutinizing financial statements, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, to assess a company’s operational efficiency, profitability, and overall financial stability. Analysts examine key performance indicators such as revenue growth, profit margins, return on equity (ROE), and debt-to-equity ratios to gauge a company’s financial trajectory.

Beyond financial metrics, fundamental analysis encompasses qualitative factors that significantly impact a company’s long-term prospects. These include management competence, competitive advantages, market position, industry trends, and regulatory environment. The quality of leadership, corporate governance practices, and strategic initiatives play crucial roles in determining a company’s ability to navigate challenges and capitalize on opportunities. Experienced analysts also evaluate a company’s research and development investments, brand strength, and customer loyalty as indicators of future growth potential.
In 2025’s complex market landscape, fundamental analysis has evolved to incorporate broader economic considerations, including interest rate trends, inflation metrics, and geopolitical factors. Modern fundamental analysis also increasingly integrates ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) metrics, reflecting growing investor emphasis on sustainable business practices. The most effective fundamental analysis combines these quantitative and qualitative elements to develop a comprehensive understanding of a company’s intrinsic value and long-term growth potential.
Technical Analysis: Decoding Market Patterns
Technical analysis serves as a powerful methodology for decoding market patterns and price movements through statistical evaluation of historical trading data. Unlike fundamental analysis, which focuses on a company’s financial health, technical analysis examines market psychology, price action, and volume trends to identify potential trading opportunities. Chart patterns such as head and shoulders, double tops and bottoms, and triangle formations provide visual representations of market sentiment and potential price reversals, enabling traders to anticipate future price movements with greater accuracy.
Key technical indicators form the backbone of this analytical approach, with moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), and Bollinger Bands being particularly valuable for market timing decisions. These indicators help identify overbought or oversold conditions, trend strength, momentum shifts, and potential support and resistance levels. Technical analysts also employ volume analysis to confirm price movements, as increasing volume typically validates the strength of a particular trend, while declining volume may signal potential reversals.
In 2025’s technology-driven market environment, technical analysis has been revolutionized by artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms that can identify complex patterns across multiple timeframes simultaneously. Modern technical analysis platforms now incorporate sentiment analysis from social media, news sources, and alternative data sets to provide a more comprehensive view of market dynamics. Successful technical analysts combine these advanced tools with traditional chart reading skills to develop robust trading strategies that adapt to changing market conditions.
Valuation Metrics and Models
Valuation metrics and models provide investors with quantitative frameworks to assess a stock’s intrinsic value relative to its market price. The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio remains one of the most widely used valuation metrics, comparing a company’s share price to its earnings per share, with the current average P/E ratio for S&P 500 companies at 26.1 as of March 2025. Other essential valuation ratios include Price-to-Sales (P/S), Price-to-Book (P/B), and Enterprise Value-to-EBITDA (EV/EBITDA), each offering unique perspectives on a company’s relative valuation compared to its peers and historical averages.
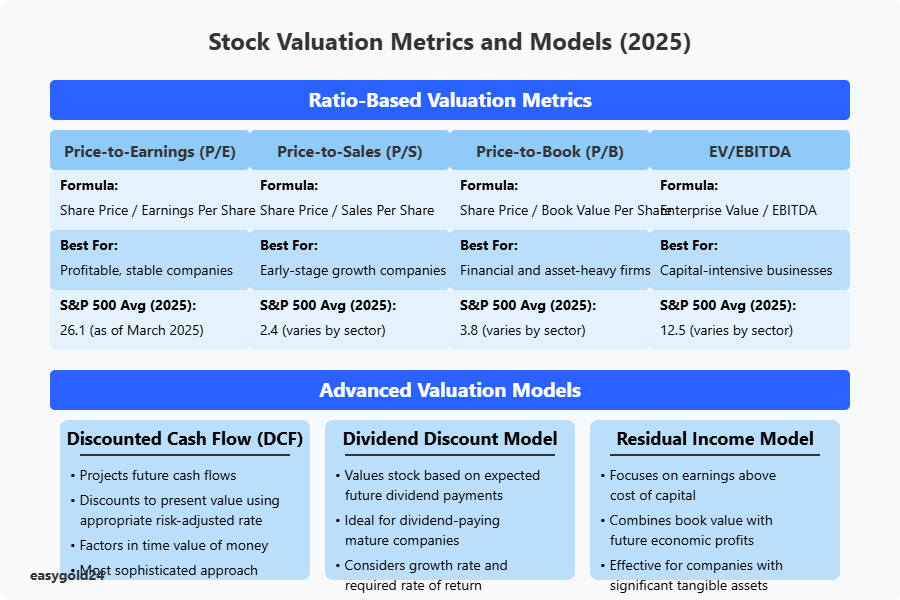
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis represents a more sophisticated valuation approach, calculating a company’s present value based on projected future cash flows. This model factors in the time value of money by discounting future cash flows using an appropriate rate that reflects the company’s risk profile. In 2025, DCF models have evolved to incorporate more nuanced variables, including variable growth rates, terminal value calculations, and sensitivity analyses that account for different economic scenarios. Sophisticated investors often combine multiple valuation methodologies to develop a valuation range rather than a single target price.
Dividend discount models and residual income models provide alternative valuation frameworks particularly suited for income-oriented investments. The dividend discount model calculates a stock’s intrinsic value based on the present value of expected future dividends, while residual income models focus on a company’s ability to generate earnings above its cost of capital. Modern valuation approaches also increasingly incorporate non-traditional metrics like customer acquisition costs, lifetime value calculations, and platform economics for technology and subscription-based businesses, reflecting the evolving nature of business models in 2025’s economy.
Risk Assessment and Management Strategies
Effective risk assessment and management strategies form the cornerstone of successful investment portfolios in today’s volatile markets. Portfolio diversification remains the most fundamental risk management technique, with research from J.P. Morgan Asset Management highlighting that diversified portfolios including bonds and alternative assets delivered 15% higher risk-adjusted returns than equity-only portfolios in recent market cycles. Diversification across asset classes, sectors, geographies, and market capitalizations helps mitigate the impact of sector-specific downturns and systematic risks that affect entire markets.
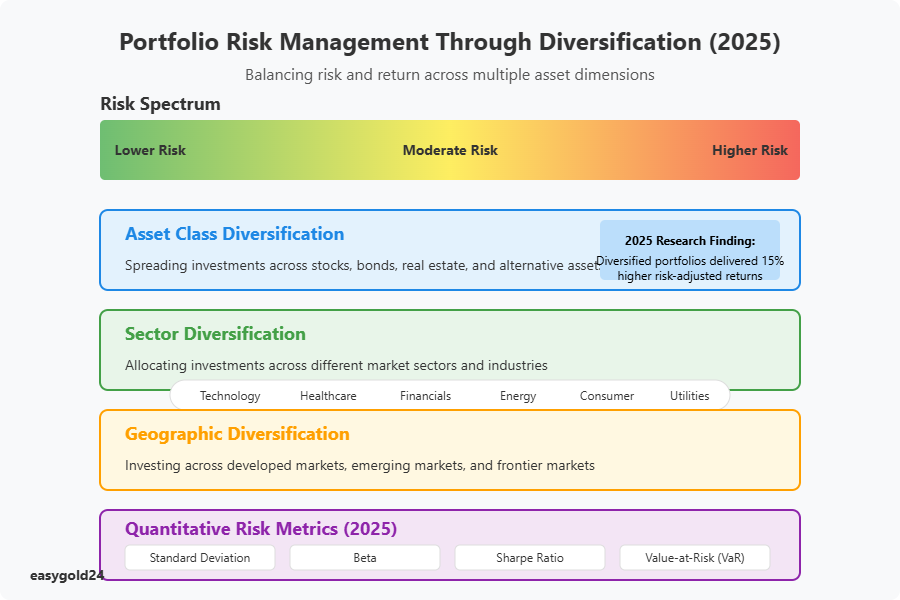
Quantitative risk metrics provide investors with statistical tools to measure and manage portfolio risk. Standard deviation quantifies volatility by measuring the dispersion of returns from their average, with higher values indicating increased risk. Beta measures a stock’s sensitivity to market movements, while the Sharpe ratio evaluates risk-adjusted returns by comparing portfolio performance to risk-free rates. In 2025, sophisticated risk management platforms employ value-at-risk (VaR) calculations and conditional value-at-risk (CVaR) models to estimate potential losses under various market scenarios, enabling investors to stress-test portfolios against extreme events.
Modern risk management increasingly incorporates alternative data sources and artificial intelligence to identify emerging risks before they manifest in traditional metrics. Sentiment analysis of news feeds, social media trends, and alternative data like satellite imagery and mobile payment patterns can provide early warning signals of changing market conditions. Portfolio hedging strategies using options, inverse ETFs, or volatility instruments have also evolved to provide more precise protection against specific risk factors. The most successful investors in 2025’s market environment adopt a dynamic risk management approach that continuously reassesses exposures and adjusts protective measures as market conditions evolve.
Sector Analysis and Industry Trends
Sector analysis plays a crucial role in identifying investment opportunities by evaluating industry-specific dynamics and growth trajectories. Different sectors exhibit varying sensitivity to economic cycles, interest rate fluctuations, and technological disruptions, making sector-specific research essential for portfolio construction. In 2025, technology and healthcare continue to demonstrate strong structural growth prospects, while energy sectors navigate complex transitions toward renewable sources. Financial sector performance remains closely tied to interest rate policies, with Morningstar research indicating that financial stocks traded at a 5% discount to fair value as of March 2025, potentially offering value opportunities.
Industry trend analysis requires examining both cyclical patterns and secular shifts that reshape competitive landscapes. Key indicators include industry concentration ratios, pricing power dynamics, regulatory developments, and technological adoption rates. The most promising investment opportunities often emerge at the intersection of multiple favorable trends, such as sectors benefiting from both demographic shifts and technological innovation. Sector rotation strategies, which involve shifting capital between sectors based on economic cycle positioning, have demonstrated effectiveness in maximizing returns through different market phases.
In 2025’s increasingly interconnected global economy, understanding cross-border industry dynamics has become essential for comprehensive sector analysis. Supply chain resilience, geopolitical factors, and regional regulatory divergences significantly impact sector performance across different markets. Industry experts recommend complementing traditional sector classification systems with thematic analyses that capture emerging business models and cross-sector convergence. The most sophisticated sector analysis frameworks incorporate alternative data sources such as patent filings, executive sentiment indicators, and real-time consumer spending patterns to identify industry inflection points before they become widely recognized.
Market Timing and Behavioral Finance
Market timing strategies attempt to predict optimal entry and exit points for investments based on various indicators and market conditions. While perfect market timing remains elusive, research indicates that avoiding the worst market days can significantly impact long-term returns. However, studies consistently show that most active timing strategies underperform buy-and-hold approaches over extended periods. Rather than attempting to time market tops and bottoms precisely, successful investors focus on identifying relative value opportunities across market cycles and adjusting position sizes based on risk-reward ratios.
Behavioral finance insights reveal how psychological biases influence investment decisions and create market inefficiencies. Common cognitive biases include loss aversion (feeling losses more intensely than equivalent gains), recency bias (overweighting recent events), and confirmation bias (seeking information that confirms existing beliefs). These psychological patterns often lead to market overreactions, providing opportunities for disciplined investors who recognize these behavioral tendencies. Momentum effects, where securities that have performed well continue outperforming in the short term, exemplify how investor behavior can create exploitable market patterns.
In 2025’s information-rich environment, sentiment indicators have gained prominence as tools for gauging market psychology. Metrics such as the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX), put-call ratios, and investor surveys provide quantitative measures of market sentiment that often signal potential turning points when they reach extreme levels. The integration of social media sentiment analysis and natural language processing of financial news has created new sentiment indicators with predictive potential. Successful market participants combine these sentiment metrics with fundamental valuation measures to identify situations where emotional reactions have created disconnects between price and value, offering attractive entry or exit points for long-term investors.
Portfolio Construction and Optimization
Effective portfolio construction blends art and science, requiring careful consideration of investment objectives, risk tolerance, and time horizons. Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) provides a mathematical framework for optimizing asset allocation to maximize expected returns for a given level of risk. The efficient frontier concept identifies portfolios that offer the highest expected return for their level of risk, with diversification across uncorrelated assets reducing portfolio volatility without necessarily sacrificing returns. In 2025’s complex market environment, traditional 60/40 stock-bond allocations have evolved into more nuanced approaches that incorporate alternative assets, factor exposures, and geographically diverse investments.
Asset allocation decisions typically exert the most significant influence on long-term portfolio performance, accounting for approximately 90% of return variability according to seminal research. Strategic asset allocation establishes long-term investment targets based on capital market assumptions, while tactical asset allocation makes shorter-term adjustments to capitalize on market dislocations or protect against anticipated volatility. Factor-based portfolio construction has gained prominence, focusing on systematic exposures to characteristics like value, momentum, quality, and low volatility that have demonstrated long-term return premiums across various market environments.
Portfolio optimization techniques have become increasingly sophisticated, incorporating advanced risk metrics beyond standard deviation. Drawdown analysis examines the magnitude and duration of portfolio declines, while tail risk measures focus on the probability of extreme losses. Correlation analysis has expanded to recognize that asset relationships often change during market stress, with dynamic correlation models providing more realistic projections of diversification benefits. The most effective portfolio construction approaches in 2025 combine quantitative optimization techniques with qualitative judgments about changing market dynamics, creating adaptive frameworks that can evolve as economic conditions and investor circumstances change over time.
Advanced Tools and Technologies for Stock Analysis
Advanced tools and technologies have revolutionized stock analysis, democratizing access to sophisticated analytical capabilities previously available only to institutional investors. AI-powered platforms now provide retail investors with comprehensive analytical frameworks that process vast datasets and identify patterns beyond human perception. Leading platforms like TrendSpider, FINQ, and Hoops AI leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze price movements, sentiment indicators, and fundamental metrics simultaneously, generating actionable insights with confidence ratings. These tools have demonstrated significant improvements in forecast accuracy, with some AI models achieving 65-75% predictive success rates for short-term price movements according to recent benchmarking studies.

Natural language processing (NLP) technologies have transformed sentiment analysis by enabling real-time evaluation of news feeds, earnings call transcripts, and social media discussions. These systems identify subtle linguistic patterns and emotional tones that often precede significant price movements, providing early indicators of changing market sentiment. Alternative data analytics platforms integrate non-traditional information sources such as satellite imagery, credit card transaction data, and mobile device patterns to gain unique insights into consumer behavior, supply chain dynamics, and business performance ahead of official financial reports.
Democratized access to quantitative trading frameworks has empowered individual investors to develop, backtest, and implement rules-based investment strategies without extensive programming knowledge. No-code platforms allow users to construct sophisticated trading systems using visual interfaces, while cloud-based backtesting environments simulate strategy performance across multiple market regimes. These technological advancements have significantly reduced barriers to quantitative investing, with the most effective tools balancing analytical power with user-friendly interfaces. As these technologies continue evolving, successful investors increasingly combine human judgment with technological capabilities, leveraging automation for data processing while applying critical thinking to strategic decisions.
Algorithmic Trading and Quantitative Analysis
Algorithmic trading has transformed market dynamics by leveraging computational power to execute trades based on predefined rules and statistical patterns. These automated systems now account for approximately 70-80% of trading volume in major markets, operating across timeframes from microsecond high-frequency trading to longer-term quantitative strategies. Algorithmic approaches offer significant advantages, including emotional discipline, consistent execution, and the ability to process multiple data streams simultaneously. The most successful algorithmic traders employ multiple strategies across different market conditions, including statistical arbitrage, trend following, mean reversion, and market making techniques.
Quantitative analysis forms the foundation of algorithmic trading, employing mathematical and statistical methods to identify market inefficiencies and tradable patterns. Machine learning algorithms have significantly enhanced quantitative capabilities by recognizing complex, non-linear relationships in financial data that traditional statistical methods might miss. Sophisticated quantitative strategies incorporate features like regime detection, which automatically adjusts trading parameters based on prevailing market conditions, and adaptive learning mechanisms that continuously refine models as new data becomes available. Research indicates that balanced quantitative approaches combining multiple uncorrelated signals typically outperform single-factor models in terms of risk-adjusted returns over complete market cycles.
The democratization of algorithmic trading tools has expanded access beyond institutional investors, with platforms like QuantConnect, TradingView, and AlgoTrader providing retail traders with professional-grade development environments. These platforms enable strategy development, backtesting against historical data, forward testing with paper trading, and eventual deployment to live markets through brokerage API connections. The most effective algorithmic traders maintain a robust development methodology, including out-of-sample testing, walk-forward optimization, and Monte Carlo simulations to evaluate strategy robustness. While automation offers numerous advantages, successful implementation requires careful risk management, including position sizing rules, correlation analysis, and circuit breakers that halt trading during unexpected market conditions.
ESG Integration in Stock Analysis
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) integration has evolved from a niche consideration to a mainstream component of comprehensive stock analysis. Research consistently demonstrates that companies with strong ESG profiles tend to exhibit lower volatility, reduced regulatory and reputational risks, and more sustainable long-term growth prospects. In 2025, approximately 40% of global professionally managed assets incorporate ESG factors, with growth particularly pronounced among institutional investors and younger retail investors. Beyond ethical considerations, ESG analysis provides valuable insights into operational efficiency, management quality, and long-term business resilience that traditional financial metrics might miss.

ESG metrics have become increasingly standardized and quantifiable, facilitating more rigorous analysis and comparison across companies and sectors. Key environmental metrics include carbon emissions intensity, resource efficiency, and circular economy initiatives. Social considerations encompass labor practices, diversity and inclusion metrics, and community relations. Governance analysis evaluates board independence, executive compensation structures, and shareholder rights protections. Sophisticated ESG analysis frameworks recognize sector-specific materiality, focusing on the environmental, social, and governance factors most relevant to particular industries rather than applying uniform criteria across all companies.
The integration of ESG factors into valuation models has become more sophisticated, with approaches ranging from ESG risk premium adjustments in discount rates to scenario-based analysis of potential regulatory changes. Climate risk modeling has gained particular prominence, with investors increasingly evaluating both transition risks (policy changes, technology shifts) and physical risks (extreme weather events, resource scarcity) within their analytical frameworks. ESG-focused thematic investments targeting specific sustainability trends—such as clean energy, water management, and circular economy—have demonstrated strong performance, with several sustainability-themed indices outperforming broader markets over recent years. In 2025, the most effective stock analysis approaches treat ESG not as a separate consideration but as an integral component of comprehensive business evaluation.
International Markets and Global Investing
International markets offer significant diversification benefits and growth opportunities beyond domestic investments, with emerging markets projected to account for approximately 65% of global economic growth through 2030 according to Goldman Sachs research. Global investing requires understanding unique market characteristics, including regulatory frameworks, accounting standards, political stability, and currency dynamics that can significantly impact investment outcomes. In 2025, several emerging markets trade at compelling valuations, with price-to-earnings ratios approximately 30% below developed markets despite stronger projected earnings growth, potentially offering attractive risk-adjusted return opportunities for investors with appropriate risk tolerance.
Country-specific analysis forms an essential component of international investing strategy, evaluating factors such as demographic trends, economic development stage, policy stability, and capital market maturity. Macroeconomic indicators including GDP growth, inflation rates, current account balances, and debt levels provide important context for assessing country risk premiums. Central bank policies and currency valuations significantly influence returns for international investors, with currency movements sometimes exceeding local market returns in determining total investment outcomes. Sophisticated global investors employ currency hedging strategies selectively, considering both hedging costs and currency trend expectations.
Global sector allocation represents an increasingly important dimension of international investing, with sector performance often diverging more significantly than country performance in recent years. This trend reflects the growing integration of global supply chains and the influence of worldwide technological trends that transcend national boundaries. In 2025, effective international investment approaches typically combine country allocation, sector positioning, and security selection within a unified framework. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs), American Depositary Receipts (ADRs), and global thematic portfolios have democratized international investing, providing retail investors with efficient access to diversified global exposures previously available only to institutional investors.
Real-Time Market Analysis and Trading Strategies
Real-time market analysis has transformed trading approaches by providing instantaneous insights into market movements, order flow dynamics, and evolving sentiment patterns. Advanced trading platforms now deliver comprehensive real-time analytics, including depth of market visualizations, volume profile analysis, and order flow indicators that reveal institutional positioning. These tools help traders identify liquidity zones, potential price inflection points, and market microstructure patterns that can drive short-term price movements. In high-velocity market environments, the ability to process and act on real-time information provides significant advantages for traders executing tactical positions.
Day trading and swing trading strategies leverage real-time analysis to identify short-term opportunities based on momentum, mean reversion, and volatility patterns. Momentum strategies capitalize on continuation patterns, entering positions in the direction of established trends during temporary pullbacks or consolidations. Mean reversion approaches seek to identify overbought or oversold conditions where prices have temporarily diverged from equilibrium levels, anticipating a return to average values. Volatility-based strategies exploit periods of expanded or contracted price movement, adjusting position sizing and profit targets based on current market conditions rather than fixed parameters.
Risk management assumes paramount importance in real-time trading environments, with professional traders typically limiting individual position exposure to 1-2% of total capital. Stop-loss orders, trailing stops, and options hedging strategies provide mechanisms for defining maximum acceptable losses before entering positions. Position sizing methodologies like fixed fractional or volatility-adjusted approaches help normalize risk across different market conditions. The psychological dimension of real-time trading cannot be overlooked, with successful traders developing robust emotional discipline and decision frameworks that prevent impulsive reactions to market movements. While technological tools provide analytical advantages, the most consistent real-time traders combine these capabilities with well-defined trading plans that specify entry criteria, exit conditions, and risk parameters for each trade.
Investor Psychology and Decision-Making
Investor psychology plays a pivotal role in financial decision-making, often influencing market outcomes more significantly than fundamental factors during periods of heightened uncertainty. Cognitive biases such as anchoring (relying too heavily on initial information), herding (following group behavior), and availability bias (overweighting easily recalled information) frequently lead investors to suboptimal decisions. Research in behavioral finance consistently demonstrates that emotional reactions to market movements can drive investors to buy high and sell low, with the average equity fund investor underperforming market indices by approximately 1.5-2% annually due primarily to poorly timed entry and exit decisions rather than fund selection.

Developing psychological resilience represents a critical component of successful investing, enabling rational decision-making during market stress when emotions typically overwhelm logical analysis. Practical approaches include maintaining decision journals that document investment rationales, implementing rules-based frameworks that reduce discretionary choices during volatile periods, and establishing predetermined investment plans that specify actions under various market scenarios. Some professional investors adopt formalized checklists to ensure comprehensive analysis before making decisions, systematically addressing both fundamental considerations and potential cognitive biases.
Contrarian investing strategies explicitly leverage crowd psychology by identifying situations where emotional overreactions have created disconnects between price and value. These approaches require significant psychological discipline, as they involve positioning against prevailing sentiment and often experiencing short-term underperformance before theses play out. The most psychologically adept investors cultivate self-awareness about their emotional tendencies and implement structural safeguards against their personal biases. In 2025’s information-saturated environment, developing disciplined information consumption habits and distinguishing between noise and signal has become increasingly important for maintaining psychological equilibrium and making sound investment decisions.
Future Trends in Stock Analysis for 2025 and Beyond
The future of stock analysis is being shaped by transformative technological advances, with artificial intelligence and machine learning systems capable of processing unprecedented volumes of structured and unstructured data. Next-generation AI platforms are moving beyond pattern recognition toward causal inference, identifying relationships between economic variables, corporate decisions, and market outcomes that provide deeper insights into future performance. Natural language processing capabilities have evolved to comprehend nuanced financial concepts across multiple languages, enabling global sentiment analysis with greater precision than previously possible. As these technologies mature, the integration of alternative data sources—including satellite imagery, Internet of Things sensors, and digital engagement metrics—is creating multidimensional analytical frameworks that capture business performance indicators well before they appear in financial statements.
Decentralized finance and blockchain technologies are creating new paradigms for market structure and corporate governance that will fundamentally alter traditional stock analysis approaches. Tokenization of assets is blurring boundaries between public and private markets, while smart contracts enable automated dividend distributions, voting mechanisms, and corporate actions with unprecedented transparency. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) represent entirely new corporate structures that require specialized analytical frameworks. As traditional distinctions between equity, debt, and hybrid securities evolve in this landscape, analysts are developing integrated approaches that evaluate total capital structure efficiency rather than treating these components separately.
Geopolitical realignment and deglobalization trends are creating more complex international investment environments that require sophisticated country risk assessment methodologies. Supply chain reconfiguration, technology decoupling, and strategic resource nationalism are creating divergent regional growth trajectories that manifest in sector-specific opportunities and challenges. Climate adaptation requirements are increasingly influencing capital allocation decisions, with physical risk assessment becoming an integral component of comprehensive investment analysis. The most forward-thinking investment professionals are developing cross-disciplinary expertise that integrates traditional financial analysis with geopolitical understanding, technological foresight, and sustainability science to navigate this evolving landscape and identify emerging opportunities ahead of consensus recognition.
From Analysis to Action: Turning Insight into Opportunity
A clear analytical process is the foundation of every strategic investment decision. With the right tools, Sie gain more than just data — Sie build the clarity to act, the confidence to stay disciplined, and the adaptability to respond as markets evolve.
As markets shift and technologies accelerate, combining fundamental insight with data-driven methods allows Sie to evaluate opportunities in real time. But true edge comes from refining your own investment process — aligning it with your goals, your risk tolerance, and your long-term vision.
Hartmann & Benz has taken the next step by officially listing on the OTCQB market, opening the door to broader participation in our expansion strategy. The listing supports the release of tradable shares while enabling us to scale our operations — including the acquisition of raw and recycled gold as part of our asset-backed investment model.
To complement this, we’ve launched the EasyGold Security Token, combining the value of physical gold with the flexibility of a digital asset. This innovation allows Sie to participate in gold ownership without the friction of traditional storage and logistics.
The opportunity is clear: participate in a modern investment strategy backed by tangible assets and driven by a long-term vision.
Position yourself early. Shape the future with us.
