Stock Strategies
Stock Strategies That Work
Bankrate’s latest survey reveals a clear trend: 77% of U.S. adults have financial regrets—and more than one in five regret not starting their retirement savings earlier. These numbers highlight the importance of building a reliable strategy when investing in stocks.
A successful stock approach doesn’t rely on luck or market timing—it’s about aligning investment methods with long-term goals. Research shows that most individual stock pickers underperform index investing over time. That’s why nearly half of all traded fund volume now flows into passive index funds. At the same time, value investing has historically delivered more sustainable returns over extended periods.
Understanding key concepts is essential: market dynamics, trading styles, stock analysis methods, and how to measure performance over time. Whether Sie passive funds bevorzugen oder gezielt auf unterbewertete Aktien setzen – entscheidend ist ein systematischer Ansatz, der diszipliniert umgesetzt wird.
The goal is clear: build a stock portfolio that serves your financial future—not your short-term impulses.
Understanding Stock Market Strategies
A solid stock strategy serves as the foundation of successful investing. Professional investors recognize that a systematic approach filters out market noise and emotional decisions that often result in costly mistakes.
What Makes a Good Strategy
The best stock strategies should be straightforward yet effective. Your financial goals and risk tolerance should align with your chosen approach. Research shows that strategic asset allocation decisions drive nearly 94% of portfolio returns, rather than market timing or security selection.
The core elements of an effective strategy include:
- Simplicity with minimal variables to avoid curve-fitting
- Clear entry and exit rules
- Proper position sizing and risk management
- Regular performance monitoring and rebalancing
Why You Need a Strategy
Investors without a defined strategy often make decisions based on fear or greed instead of rational analysis. Studies have found that emotional traders tend to buy high during market peaks and sell low during downturns.
A well-planned strategy also provides:
- A consistent framework for decisions
- Protection against market volatility
- Better risk management
- Clear performance tracking metrics

Common Strategy Mistakes
Even expert investors make mistakes, but awareness of common pitfalls helps avoid them. The most significant problem is chasing performance—investing in assets or strategies that performed well recently without considering whether those returns can be sustained.
Another reason investors fail is inadequate diversification. Many concentrate their portfolio in single securities or sectors, which can lead to disaster when markets move against these positions.
Investors also frequently:
- Attempt to time the market instead of maintaining investments (Missing just the top 10 trading days from 1993-2013 reduced returns from 9.2% to 5.4% annually)
- Allow emotions to override their trading plan
- Ignore transaction costs and taxes
- Focus exclusively on short-term gains
Success comes from developing a disciplined approach. Professional traders recommend beginning with thorough research to understand market fundamentals and create clear rules for entries and exits. Successful strategies also include regular portfolio rebalancing to maintain target allocations and manage risk effectively.
It’s important to note that no strategy works perfectly in all market conditions. Finding an approach that matches your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon helps you remain disciplined through market cycles. Your strategy should be sustainable during both favorable and challenging market conditions unless fundamental factors indicate a necessary change.
Choose Your Trading Style
Your trading style shapes your entire approach to the stock market. Let’s examine three proven methods traders use to generate profits.
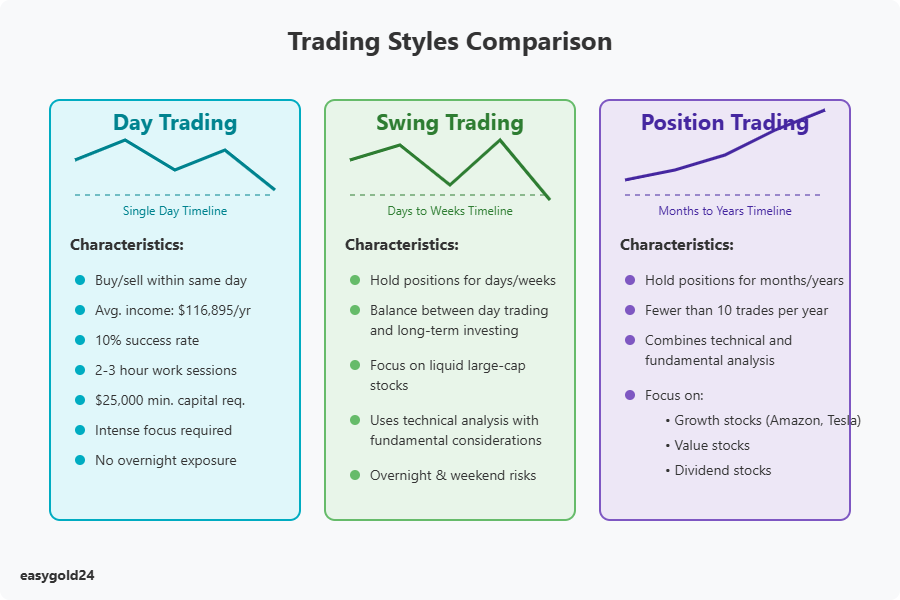
Day Trading Approach
Day trading requires intense focus and split-second decisions. Traders buy and sell securities within the same day without maintaining overnight positions. The average day trader earns $116,895 annually. However, the reality is reflected in success rates—only 10% of day traders consistently generate profits.
Day trading offers several advantages:
- Trading can occur from any location with internet access
- Work sessions typically last only 2-3 hours
- No exposure to overnight market movements
Despite these benefits, day traders face significant challenges. The strategy requires substantial initial capital, particularly given FINRA’s $25,000 minimum equity requirement for pattern day traders. Day traders also need exceptional discipline and must be comfortable with risk-taking.
Swing Trading Basics
Swing trading occupies a middle ground between day trading’s rapid pace and long-term investing. Traders hold positions for days or weeks to profit from market momentum “swings.” These traders primarily utilize technical analysis but also consider fundamental factors to enhance their selection process.
Swing traders typically focus on:
- Liquid large-cap stocks
- Technical indicators including moving averages and RSI
- Support and resistance levels
Swing trading demands less time than day trading, thereby reducing stress levels. The disadvantage, however, is that traders must accept risks from overnight and weekend gaps that may occur when markets reopen.
Position Trading Method
Position trading adopts a long-term perspective—trades can extend for months or years. These traders aim to capture major market trends rather than short-term price movements. They typically execute fewer than 10 trades annually.
Position traders thrive in bull markets with well-defined trends. They combine technical and fundamental analysis by focusing on:
- Growth stocks (Amazon and Tesla exemplify this category)
- Value stocks trading below their intrinsic worth
- Dividend stocks providing steady cash flow
This approach conserves time and reduces trading costs. The trade-off is that capital remains committed for extended periods, potentially causing investors to miss other market opportunities.
Each style suits different trader types and circumstances. Day trading appeals to quick thinkers who can monitor markets continuously. Swing trading accommodates those seeking a balance between active trading and personal time. Position trading suits patient investors comfortable with long-term market exposure. Success stems from aligning your style with your financial objectives, schedule, and risk tolerance.
Basic Stock Analysis Methods
Stock analysis methods enable investors to make informed investment decisions. Technical analysis and fundamental analysis predominate in today’s investment landscape.
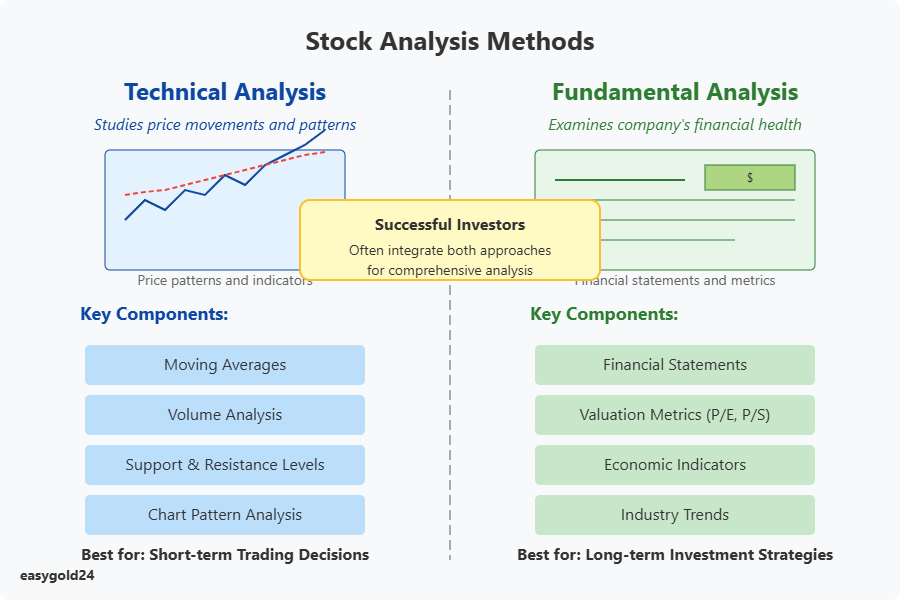
Technical Analysis Essentials
Technical analysis predicts future market behavior by examining price movements and trading volumes. This method operates on the principle that a stock’s price action incorporates all known information about the security.
Price patterns form the foundation of technical analysis. Traders analyze candlestick charts displaying open, close, high, and low prices over specific timeframes. Support and resistance levels are crucial—support indicates price levels where traders believe stocks will not decline further, while resistance identifies potential selling thresholds.
Key technical indicators include:
- Moving averages for trend identification
- Volume analysis to assess trading activity
- Relative strength measurements
- Chart pattern analysis
- Support and resistance levels
Fundamental Analysis Basics
Fundamental analysis examines a company’s financial health and market position. This approach evaluates three major components:
1 Financial Statements
- Income statements revealing revenue and expenses
- Balance sheets showing assets and liabilities
- Cash flow statements tracking monetary movements
2 Valuation Metrics The price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio serves as the primary valuation metric. Other important measurements include:
- Price-to-sales (P/S) ratio for companies without consistent earnings
- Price-to-book (P/B) ratio assessing net asset value
- Earnings per share (EPS) measuring profitability
3 Economic Indicators Analysts also evaluate broader economic factors:
- GDP growth rates
- Inflation levels
- Interest rate environments
- Industry trends
Many successful investors integrate both approaches. Technical analysis helps determine optimal entry and exit points after fundamental analysis identifies promising opportunities. For example, a trader might select potential investments using fundamental criteria and then utilize technical indicators to identify specific entry prices.
These methods function differently based on investment timeframes. Technical analysis proves most effective for short-term trading decisions because it concentrates on immediate price movements. Fundamental analysis aligns better with long-term investment strategies as it examines the underlying strength of the business.
Both methods require regular updates and adjustments. Technical analysts must monitor price movements and volume changes, while fundamental analysts track quarterly earnings reports and economic developments. By properly employing these analysis methods, investors can develop more informed approaches to stock market participation.
Create Your Trading Plan
A well-structured trading plan is essential for success in stock trading. Below are proven strategies to develop a plan that aligns with your objectives and risk tolerance.
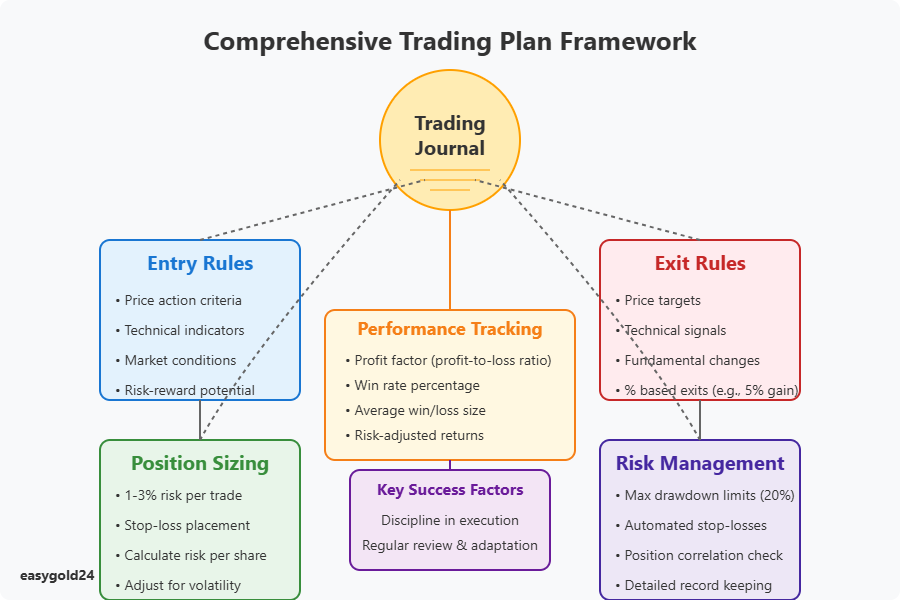
Entry Rules
You can eliminate emotional decision-making in trading by establishing objective entry rules. Begin by defining clear criteria for viable trades. Consider these key factors:
- Price action and technical indicators
- Market conditions and sentiment
- Fundamental company metrics
- Risk-reward potential
It’s crucial to understand your rationale before entering any position. Your entry strategy must align with your overall portfolio goals and investment timeline.
Exit Rules
Traders should focus equally on exits and entries. Your exit conditions should be based on:
1 Price targets—Establish profit-taking levels in advance
2 Technical signals—Look for bearish patterns or resistance
3 Fundamental changes—Verify if your original trade rationale remains valid
4 Percentage-based exits—Implement parameters such as 5% gain versus 2% loss
Adhere to your predetermined exit rules, regardless of profit or loss. Close your position immediately if market conditions no longer support your original trade thesis.
Position Sizing
Position sizing represents one of the most critical yet misunderstood aspects of trading. Novice traders should risk only 1-3% of their account on individual trades. With a $50,000 account, this means limiting risk to $500-$1,500 per position.
To calculate your position size:
- Establish your stop-loss level
- Calculate risk per share/contract
- Divide maximum risk amount by risk per share
For example, if each price tick equals $10 and your stop is 50 ticks away, one contract risks $500. Adjust your position size to maintain consistent risk levels across different securities.
Risk Management
A robust risk management system protects your trading capital. Studies indicate that successful traders prioritize capital preservation through disciplined risk control. Core components include:
- Setting maximum drawdown limits (typically under 20% of buying power)
- Using stop-loss orders to automate risk control
- Monitoring correlation between positions
- Closing all trades before overnight sessions
- Tracking open position sizes carefully
Maintain detailed records of every trade in your trading journal. Document your entry/exit points, position sizes, and rationales behind each decision. This practice facilitates improvement through performance analysis.
Note that even profitable traders experience losses—the key is managing those losses effectively. By implementing systematic approaches to entries, exits, position sizing, and risk management, you create a framework for sustainable trading success. Maintain discipline in executing your plan across all market conditions.
Track and Improve Performance
Your trading performance will improve with proper monitoring and analysis of your stock strategies. Here are proven methods to track and enhance your trading results.
Keep a Trading Journal
A trading journal functions as your personal performance database. Studies show traders who maintain detailed records can better identify their strengths and weaknesses. Your journal should include these essential elements:
- Date and time of trades
- Traded products/contracts
- Position sizes
- Trade direction/strategy
- Entry price and timing
- Exit price and timing
- Profit/loss outcomes
- Market condition analysis
- Psychological state
Numerous trading journal software applications exist today, although even a basic spreadsheet or notebook suffices. Success derives from consistent and thorough trade documentation. Recording your emotional state before, during, and after trades helps identify psychological biases affecting your decisions.
Review Your Trades
Analysis of past trades provides valuable insights for strategy refinement. Professional traders recommend dedicating at least 30 minutes daily to reviewing your trading activities. A systematic review helps you:
- Identify profitable setups and market conditions
- Recognize patterns in winning and losing trades
- Evaluate risk management effectiveness
- Assess emotional discipline
Key metrics to consider when reviewing performance include:
- Profit factor (ratio of profits to losses)
- Win rate percentage
- Average win/loss size
- Risk-adjusted returns
Backtesting is essential for performance enhancement. This process tests your strategies against historical data to confirm their effectiveness. During backtesting, examine:
- Strategy definition (entry/exit rules)
- Historical data collection
- Implementation on testing platform
- Results analysis
- Strategy optimization
Your trading journal helps quickly identify common mistakes. For instance, one trader discovered poor results from intraday scalping and successfully modified their strategy. Your journal might reveal patterns such as:
- Taking profits prematurely
- Allowing losses to accumulate excessively
- Incorrect position sizing
- Poor market condition selection
Trading success requires continuous learning and adaptation. Detailed records and regular performance reviews create a feedback loop for ongoing improvement. Additionally, portfolio management applications offer benefits including real-time monitoring, asset allocation tracking, and performance measurement.
Thorough tracking and analysis will deepen your understanding of trading strengths and areas needing improvement. This comprehensive approach to performance review helps refine your stock strategies and enhance long-term trading results.
Build Smarter with Strategy—Invest with Purpose
Stock investing is more than buying into strong companies. It’s about designing a strategy that reflects your mindset, time horizon, and financial goals. Whether Sie kurzfristig handeln oder langfristig Vermögen aufbauen möchten – entscheidend ist ein disziplinierter, methodischer Ansatz.
At EasyGold, we understand how essential that mindset is. That’s why our mission goes beyond traditional investment approaches. With Hartmann & Benz now officially listed on the OTCQB market, we’ve opened new opportunities for international investors to participate in our long-term vision. This includes the launch of the EasyGold Security Token—designed to simplify digital gold ownership while reducing transaction costs and eliminating the need for physical storage.
Our OTCQB listing marks a key step in our development. It reflects our commitment to transparency, regulatory compliance, and strategic growth. Funds raised through public investment directly support the acquisition of raw and recycled gold, forming the foundation for our tokenized asset ecosystem.
For those seeking to combine traditional investment principles with modern market access—this is your opportunity to act.

